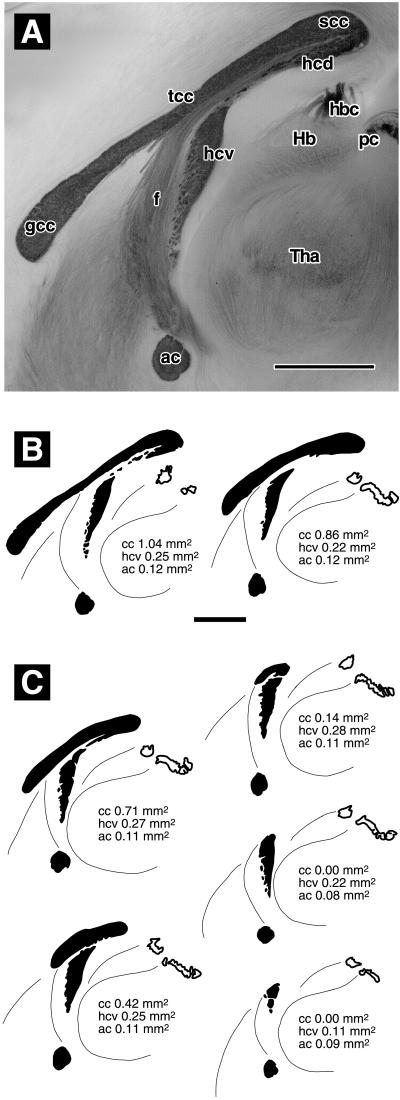
Figure 1.
Classification of forebrain commissures in brains that were split in the midsagittal plane and stained with gold chloride. (A) C57BL/6 mouse with normal commissures. The anterior (ac) and ventral hippocampal (hcv) commissures are darkly stained, as are the genu (gcc), truncus (tcc), and splenium (scc) of the corpus callosum. There is no clear boundary between the dorsal hippocampal commissure (hcd) and the splenium. Fibers of the fornix (f) stain more weakly. They emerge along the ventral surface of the truncus, then run ventrally and rostrally parallel to the sectioning plane. Hb, Habenula; hbc, habenular commissure; pc, posterior commissure; Tha, thalamus. (B) Representative camera lucida drawings of commissures classified as normal: (Left) C57BL/6 (same brain as in A), (Right) a wild type of line βAPPΔ/Δ Sv. (C) Representative camera lucida drawings of commissures classified as abnormal. From top left to bottom right: slightly reduced corpus callosum (cc), strongly reduced corpus callosum, rudimentary corpus callosum, absent corpus callosum with still normal ventral hippocampal commissure, and absent corpus callosum with reduced ventral hippocampal commissure. (Bar in A = 1 mm. Bar in B = 1 mm, applies to B and C.) See text for details.