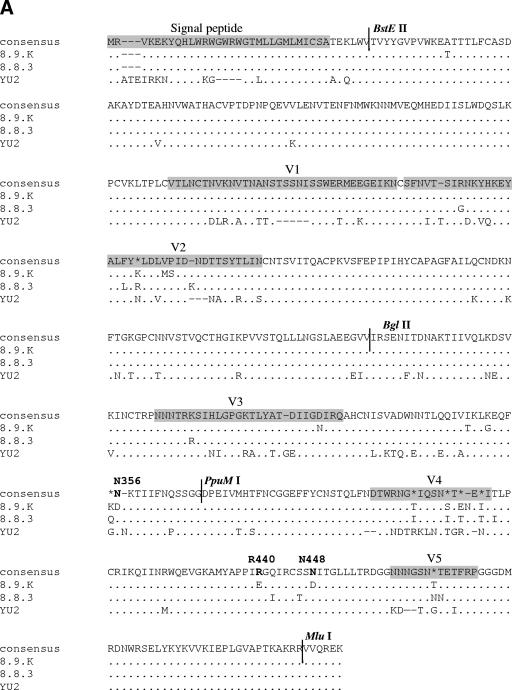
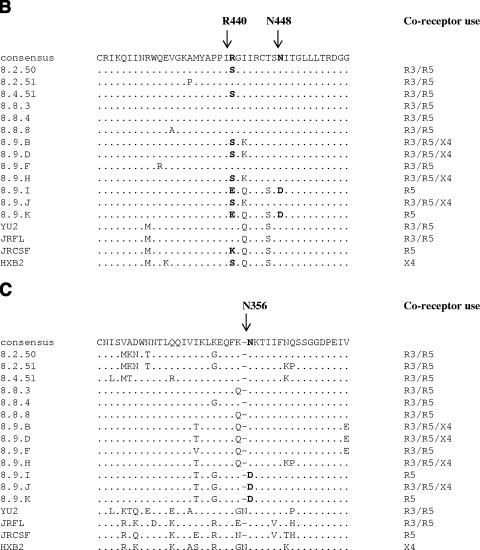
FIG.2.
Env alignments. (A) Amino acid alignments (generated using ClustalW [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustralw]) of the R5-only-using Env 8.9.K (GenBank accession number DQ645384), the most closely related R3/R5-using Env 8.8.3 (GenBank accession number DQ425072), and the prototypical R3/R5-using Env YU2 (GenBank accession number M93258). The asterisks indicate lack of consensus between the three Envs. The dots indicate residues identical to those in the consensus sequence, and the dashes indicate gaps. The signal peptide and the gp120 variable loops are shaded gray. The locations of the sites for the restriction enzymes BglII, BstEII, MluI, and PpuMI used for the sequence swapping are also indicated. Residues subjected to site-directed mutagenesis are in boldface. (B) Alignments of a section of the C4 regions of all patient Envs (GenBank accession numbers AY295233, AY295235, AY295237, DQ425072 to -4, and DQ64378 to -84) and Envs YU2, JRFL, JRCSF, and HXB2 (GenBank accession numbers M93258, AY669728, M38429, and K03455, respectively). The dots indicate residues identical to those in the consensus sequence, and the dashes indicate gaps. The determinants for CCR3 use are in boldface. (C) Alignments of a section of the C3 Env regions (see description of panel B).