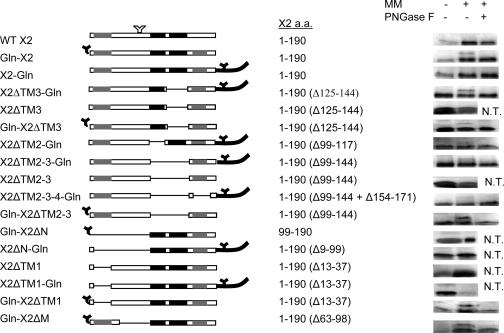
FIG. 7.
In vitro glycosylation assays of wild-type or mutated X2. On the left is a schematic representation of the various X2 constructs. The predicted transmembrane domains are shown with gray and black boxes as in Fig. 1. Amino acids (a.a.) inserted at the N or C termini of the proteins are shown with dark lines. Introduced N-glycosylation signals are represented by black Y's. A naturally occurring putative N-glycosylation site is shown by the white Y, although this site was not recognized in any of the mutants tested. The dashed lines represent deleted regions within X2. The name of each construct is indicated on the left, and the amino acids of the X2 domain contained in each construct are indicated in the middle. In vitro glycosylation assays are shown on the right. Each protein was translated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of canine microsomal membranes (MM). The translation products were further treated with endoglycosydase F (PNGase F), separated by SDS-PAGE, and detected by autoradiography. Only the relevant portions of the gels are shown. N.T., not tested.