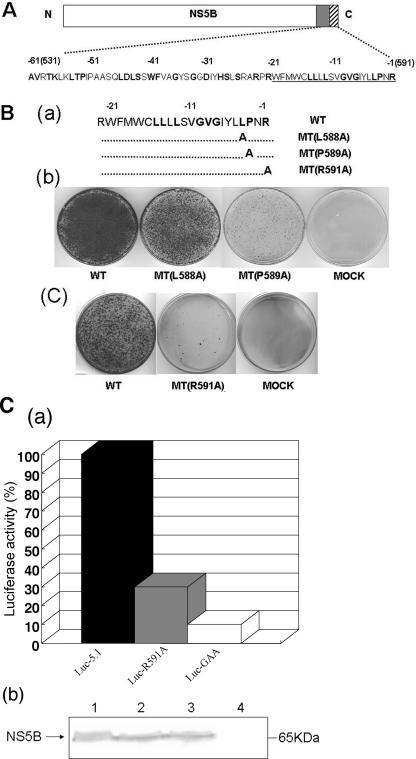
FIG. 2.
Mutational analyses of some conserved amino acids in the HCV NS5B C-terminal transmembrane domain. (A) NS5B is divided into three functional motifs. The catalytic domain (open box) of NS5B contains the N-terminal 530 amino acids of the protein, which is followed by the noncatalytic region (aa 530 to 591) at the C terminus. Highly conserved amino acids are shown as boldface letters. Underlined amino acid residues correspond to the transmembrane domain of NS5B (hatched box). Negative numbers above the amino acid sequences represent the amino acid positions counted backward from the C-terminal end of the NS5B protein. (B) Effect of point mutations in the NS5B transmembrane domain on the colony-forming efficiency of the subgenomic replicon. (a) Amino acid sequences of the transmembrane domains of wt and mutant NS5B proteins. (b and c) In vitro RNA transcripts of the wt and mutant replicon constructs were transfected into Huh-7 cells, and the colony-forming efficiency of the replicons was measured as described in Materials and Methods. (C) (a) Effect of the R591A mutation in NS5B on transient replication. Huh-7 cells were transfected with the specified luciferase replicons, and luciferase activities were determined in lysates of cells harvested 4 and 72 h after transfection. The 4-h value (not shown) was used to correct for different transfection efficiencies. The 72-h value of luc-5.1 (7.2 × 103 units) was set as 100%. Data are means of three independent experiments. (b) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts from naïve and luciferase replicon-transfected Huh-7 cells. Western blot analysis was carried out as described in Materials and Methods with polyclonal antibody to NS5B. Lane 1, luc-5.1-transfected cells; lane 2, luc-R591A-transfected cells; lane 3, luc-GAA-transfected cells; lane 4, naïve Huh-7 cells.