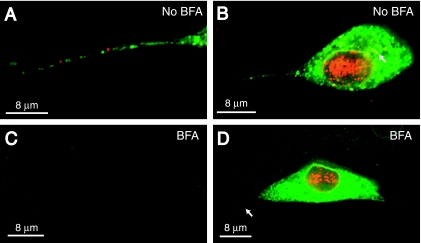
FIG. 7.
Effects of BFA on axonal transport of HSV capsids and glycoproteins. SK-N-SH neurons were infected with HSV-1 (F) and either not treated or treated with BFA (2 μg/ml) from 3 h until 15 h after infection. Neurons were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with a combination of mouse anti-VP5 MAb (red) and rabbit polyclonal gE/gI-specific antibodies (green) followed by Texas red-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG and FITC-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG. (A) Axon of neuron not treated with BFA. (B) Cell body and axon of neuron not treated with BFA. The arrow points to anti-VP5 staining in the cytoplasm. (C) Axon of neuron treated with BFA. (D) Cell body and axon of neuron treated with BFA. The arrow points to an axon extending from the neuronal cell body. Scale bars, 8 μm.