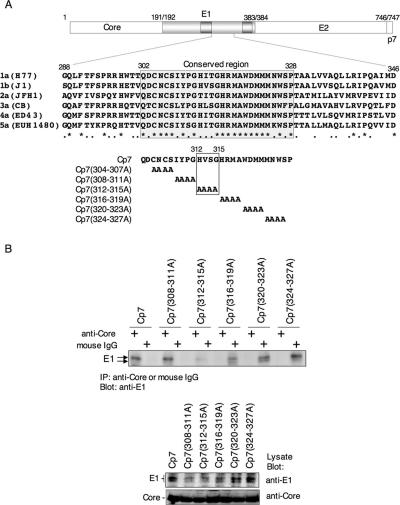
FIG. 6.
Four amino acid residues, 312 to 315, in the cytoplasmic region of the E1 protein are important for interaction with the core protein. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequence of the E1 cytoplasmic region among different HCV genotypes (1a, H77 [AF009606]; 1b, J1 [D89815]; 2a, JFH1 [AB047639]; 3a, CB [AF046866]; 4a, ED43 [Y11604]; 5a, EUH1480 [Y13184]). A conserved region from Gln302 to Pro328 is shown by gray shading. Mutant polyproteins consisting of the core, E1, E2, and p7 proteins with four residues each replaced by Ala in the conserved E1 region were constructed. Four amino acid residues, His312, Val313, Ser314, and Gly315, in the E1 cytoplasmic region of strain J1 and substitution of the amino acids with Ala in Cp7 (312-315A) are indicated by the box. (B) These mutant polyproteins were expressed in 293T cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-core antibody or nonspecific mouse IgG in the presence of MgCl2 and tRNA. The E1 protein that coprecipitated with the core protein was detected by immunoblotting. The substitution of four amino acid residues, 304 to 307, with Ala in the conserved region of the E1 protein, Cp7 (304-307A), could not be examined due to the low level of expression.