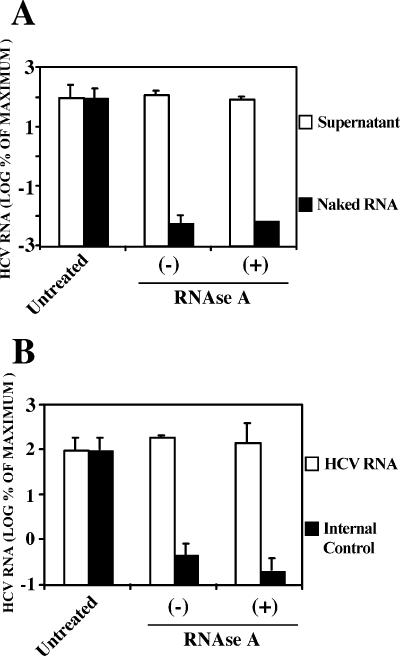
FIG. 2.
Supernatant HCV RNA is resistant to RNase A degradation. Infected cell supernatants and controls were treated with an excess of RNase A (40 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37°C. The remaining RNA was quantitated by RT-qPCR by using untreated RNAs as a reference. Results are shown as means and standard deviations (error bars) (n = 3) of the percentage of the input RNA. (A) Supernatants (white bars) or naked HCV RNA (black bars) were treated in parallel and HCV RNA was quantitated by RT-qPCR in the different samples. (B) An internal naked RNA control was included in the supernatant-RNase A mixture and both HCV RNA (white bars) and control RNA (black bars) were quantitated by RT-qPCR in the same sample. −, absence of; +, presence of RNase A.