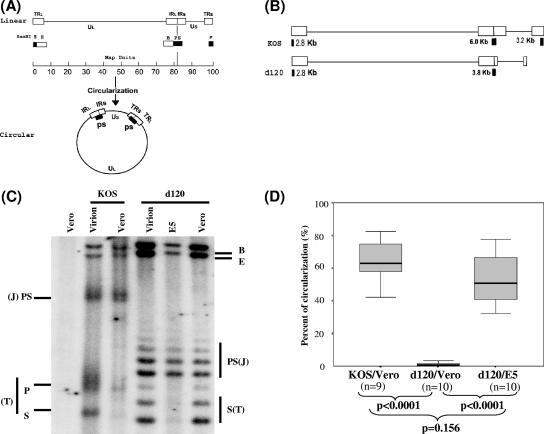
FIG. 1.
Southern blot analysis of HSV-1 DNA structures of wild-type strain KOS and ICP4-deleted mutant d120. (A) Maps of the HSV-1 genome as linear and circular forms. The linear map of the HSV-1 genome is divided into unique long (UL) and unique short (US) segments with open boxes (TRL and TRS indicate long and short terminal repeats, respectively; IRL and IRS indicate long and short inverted repeats, respectively) identifying the regions of the genome that are “repeats”. Solid boxes under the linear map show the genomic locations of terminal restriction endonuclease BamHI P and S fragments and an internal joint PS fragment, which hybridizes to radioactive probes that are generated from the BamHI PS fragment. Probes generated from BamHI B fragment hybridize to both BamHI B and E fragments, because they both contain repeat sequences. Note that BamHI P and S fragments exist only as linked PS fragments (two copies) in the circular form. (B) The size and location of the BamHI-digested terminal fragments and joint fragments of ICP4-deleted mutant d120 and the wild-type strain KOS. Please note that the boundaries of the 4.1-kb deletion in both copies of the ICP4 locus were not determined precisely in previous studies (8). After the mapping study using Southern blot hybridization, the p fragment of the d120 genome is no longer detected when the membrane was probed with the BamHI PS fragment. (C) Southern blot analysis of HSV-1 DNA structures of wild-type strain KOS and mutant d120 following infection. HSV-1 wild-type strain KOS or ICP4 mutant d120 was used to infect Vero cells or ICP4-expressing E5 cells at an MOI of 5 in the presence of PAA. Cells were harvested 3 hpi, and infected nuclear DNA was isolated. One-microgram aliquots of uninfected Vero DNA, Vero DNA with 20 ng of KOS virion, KOS-infected Vero DNA, Vero DNA with 20 ng of d120 virion, d120-infected E5 DNA, and d120-infected Vero DNA were analyzed with the 32P-labeled probes generated from BamHI PS and B fragments as described in Materials and Methods. The intensities of the bands were determined by PhosphorImager analysis and are listed in Table 1. The mobility of terminal P and S, joint PS, internal B, and E fragments identified by the probes are indicated. The joint (J) and terminal (T) fragments for each virus are also indicated. (D) Statistical analysis comparing the percent of circularization of the genome of wild-type strain KOS and mutant strain d120 following infection in Vero and E5 cells as described for panel C and as analyzed in Table 1. Note the percent of circular DNA was calculated using a previously published equation (29), as noted in Table 1. The data from 9 (n = 9) or 10 (n = 10) experiments were analyzed and are displayed as the range of data with the median, indicated as a thick line in the middle of the box, which indicates the range from the 25% quartile to the 75% quartile of the data. The P value displayed was obtained by analyzing the data using the Mann-Whitney two-tailed test.