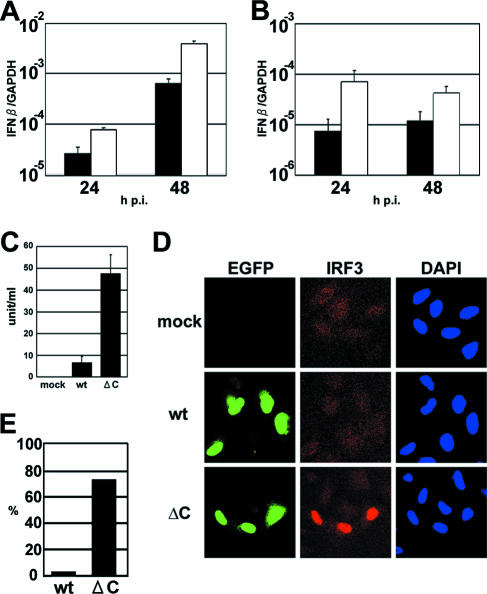
FIG. 3.
Increased IFN induction in MVΔC-infected cells. (A) Quantification of IFN-β mRNA in MVΔC-infected cells. A549/hSLAM cells were infected with MVwt or MVΔC at an MOI of 0.5. At 24 and 48 h p.i., total RNAs were extracted from the cells, and the levels of IFN-β mRNA were quantified by RT-QPCR. All data were normalized by the corresponding level of GAPDH mRNA. Filled bars, MVwt; open bars, MVΔC. The data represent the means ± standard deviations of triplicate samples. (B) IFN-β induction in a single step of growth. The experiments shown in panel A were repeated in the presence of a fusion-blocking peptide. (C) Monolayers of A549/hSLAM cells were infected with MVwt or MVΔC at an MOI of 0.5. At 48 h p.i., the amounts of IFN-β in the culture medium were determined by ELISA. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of IRF3 in virus-infected cells. A549/hSLAM cells were infected with MVwt or MVΔC at an MOI of 0.5 and incubated in the presence of a fusion-blocking peptide. At 36 h p.i., the cells were fixed and permeabilized, and IRF3 was detected by indirect immunofluorescence staining. Green and red fluorescence indicates EGFP and IRF3, respectively. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (E) The percentages of cells with nuclear localization of IRF3 relative to the total number of infected cells were determined using a fluorescence microscope.