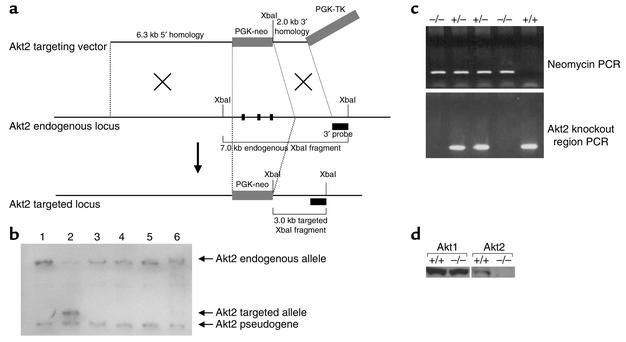
Figure 1.
Generation of Akt2-deficient mice. (a) Illustration depicting strategy for homologous recombination in DBA/1lacJ ES cells. The locations of the 3′ probe and XbaI recognition sites used for Southern blot screening of the ES cells are indicated. The PGK-neo cassette was inserted in the same orientation as the Akt2 gene. (b) Southern blot analysis of DNA isolated from ES cells transfected with the Akt2 targeting vector. Genomic DNA from six ES cell clones was isolated and digested with XbaI restriction endonuclease and hybridized with the external 1.0-kb BamHI/XbaI 3′ probe. This probe will recognize a 7.0-kb endogenous, 3.0-kb targeted, and 2.7-kb Akt2 pseudogene XbaI fragment. The probe recognizes the pseudogene due to the presence of a 3′ exon, also contained in the Akt2 pseudogene sequence. Note that only clone 2 contains the targeted allele. (c) PCR genotyping analysis of F2-generation mice. Two PCR reactions are performed on each sample; one is specific for a targeted allele (top panel) and the other is specific for the Akt2 locus within the knockout region (bottom panel). Taken together, all three genotypes, wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous (+/+, +/–, and –/–), can be determined. (d) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from brains isolated from Akt20+/+ and Akt20–/– mice. The blot to the left was hybridized with an anti-Akt1 Ab and the one to the right with an anti-Akt2 Ab.