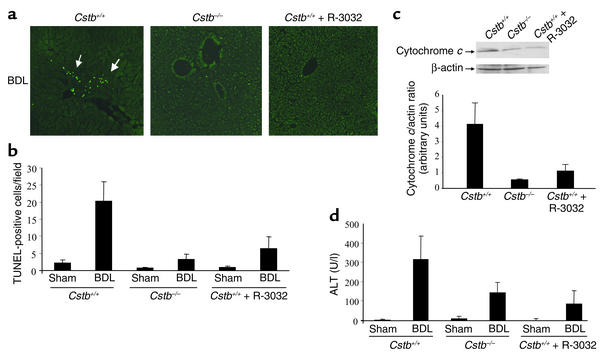
Figure 2.
Liver injury and cytochrome c release are reduced in Ctsb–/– and R-3032–treated Ctsb+/+ mice. Ctsb+/+ and Ctsb–/– mice were BDL for 3 days as described in Methods. (a) Fixed liver specimens were analyzed by TUNEL assay to identify apoptotic hepatocytes (arrows). (b) The number of TUNEL-positive cells was significantly higher in Ctsb+/+ BDL mice than in sham-operated control or Ctsb–/– and R-3032–treated Ctsb+/+ BDL mice (P < 0.0001, n = 4 for each experimental group). (c) Cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were prepared as described in Methods. Aliquots of 50 μg of cytosolic protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for cytochrome c. Release of cytochrome c in the cytosol was higher in Ctsb+/+ BDL livers compared with Ctsb–/– and R-3032–treated Ctsb+/+ BDL mice. A representative immunoblot from one animal from each group is shown, together with densitometric analysis of multiple immunoblots (n = 3 animals for each group). (d) Serum ALT values are significantly greater in Ctsb+/+ than in Ctsb–/– (P < 0.005, n = 4 for each experimental group) and R-3032–treated Ctsb+/+ mice 3 days after BDL (P < 0.0001, n = 4 for each experimental group). U/l, units per liter.