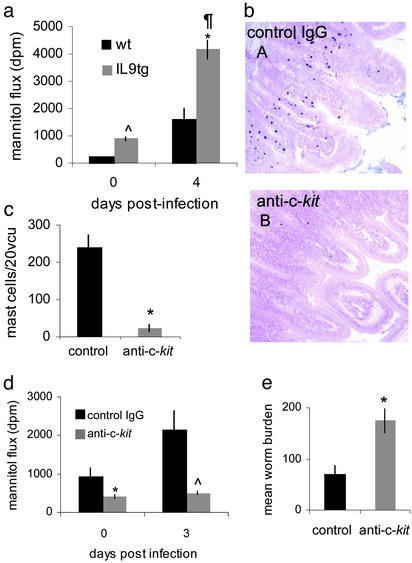
Fig. 3.
IL-9 transgenic mice overexpress mucosal mast cells and enhance intestinal permeability. Intestinal permeability was compared between IL-9 transgenic (tg) mice and WT (wt) mice at days 0 and 4 postinfection. Λ, P < 0.002 wt vs. IL-9tg d0; *, P < 0.001 IL9tg d0 vs. d4 postinfection; ¶, P < 0.002 wt vs. IL-9tg d4 postinfection (a). Anti-c-kit antibody blocked mucosal mastocytosis in IL-9tg mice at d4 postinfection (bB) compared with infected control IgG-treated mice (bA), magnification ×200. Numbers of mast cells per 20 VCUs were counted in anti-c-kit-treated IL-9 tg mice compared with control IgG-treated mice; *, P < 0.03 (c). Anti-c-kit blocked enhanced mucosal permeability at d0 and d3 postinfection compared with IL-9 tg mice treated with control IgG antibodies, *, P < 0.03 control IgG vs. anti-c-kit d0; Λ, P < 0.05 control IgG vs. anti-c-kit d3 (d). Anti-c-kit antibody delayed worm expulsion compared with mice treated with control antibody; *, P < 0.02 (e).