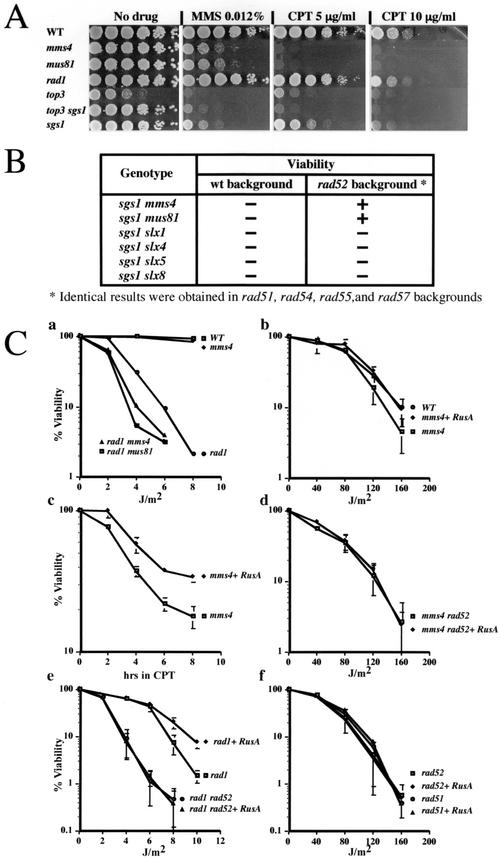
FIG.6.
MUS81-MMS4 functions downstream of homologous recombination. (A) S. cerevisiae strains with the indicated genotypes were concentrated to an optical density at 600 nm of 3.0 and serially diluted 10-fold, and approximately 5-μl volumes were spotted on YPD (38) plates containing the indicated drug. Plates were photographed following 3 days of growth at 30°C. WT, wild type. (B) The indicated double and triple mutants were constructed by genetic crosses between appropriately marked strains, some of which carried a complementing SGS1/URA3 plasmid (34). Following sporulation and tetrad dissection, the viability of the meiotic segregants was determined by attempting to eliminate the SGS1/URA3 plasmid by growth on medium containing 5-fluoroorotic acid. wt, wild type. (C, part a) Yeast cells with the indicated genotypes were spread on YPD plates and irradiated with UV light, and viability was determined following 3 days of growth at 30°C. (C, parts b to f) Yeast cells carrying an empty vector (pRS415) or the RusA expression plasmid (pKR6980) were spread on the appropriate selective plates and treated as in the experiment whose results are shown in part a. For CPT sensitivity testing, yeast cells were grown in selective medium containing CPT at 5 μg/ml. After the indicated times, aliquots of cells were removed, washed once, and plated on selective plates lacking CPT. Viability was then determined following 3 days of growth at 30°C. WT, wild type.