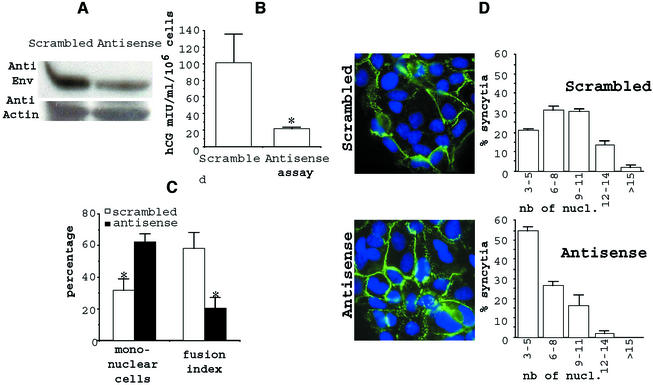
FIG. 6.
Specific inhibition of HERV-W env expression reduces syncytium formation and hCG secretion. After 5 h of culture, the primary cytotrophoblasts were transfected with random (Scrambled) or HERV-W specific (Antisense) oligonucleotides. (A) Western blot analysis of Env glycoprotein in the cell lysates in the absence (Scrambled) or presence (Antisense) of HERV-W- specific oligonucleotides. Detection was done with the anti-SU polyclonal antibody and standardization using an anti-actin monoclonal antibody. (B) hCG titration in the absence (Scrambled) or presence (Antisense) of HERV-W-specific oligonucleotides. (C) After 48 h of culture, the fusion activity of the envelope glycoproteins was determined. The cells were fixed, immunostained with anti-desmoplakin monoclonal antibody, and counterstained with DAPI. Mononuclear cells were counted, and the fusion index (7) was determined as (N − S)/T, where N is the number of nuclei in the syncytia, S is the number of syncytia, and T is the total number of nuclei counted. Results are expressed as percentages of the fusion indices. (D) Large syncytia were observed using random oligonucleotide (scrambled), and smaller ones were observed using HERV-W-specific oligonucleotides (antisense). The nucleus distribution was evaluated as followed: 100 syncytia were scored after staining, and the nuclei were counted in each syncytium. Data from one representative experiment are expressed as the distribution of syncytia as a function of the number of nuclei per syncytium. Three coverslips incubated in separate wells of a six-well microplate were observed (means and SEM) for each incubation condition. *, P < 0.05.