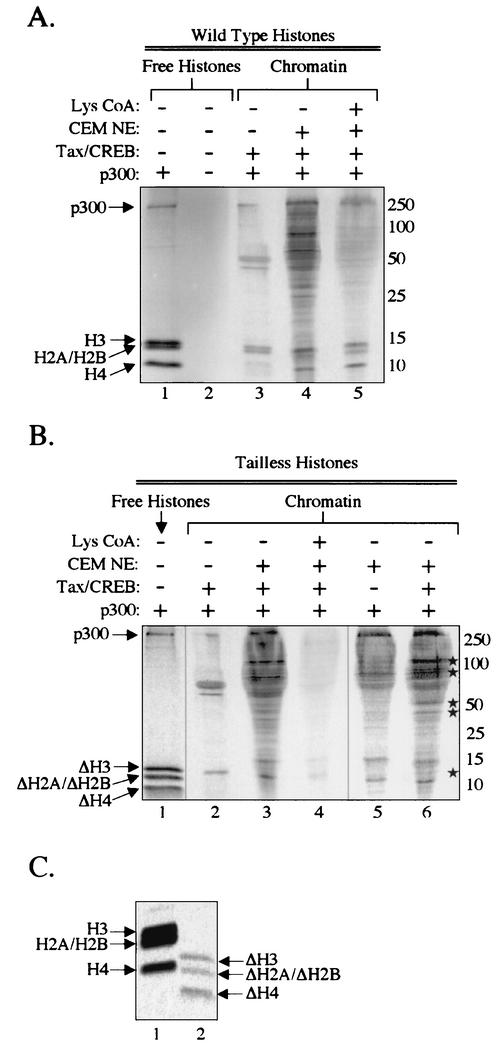
FIG. 9.
Histone tail-independent acetylation of nuclear extract proteins by CBP/p300. Chromatin templates were assembled with NAP-1, ACF, and wild-type or tailless histones, as indicated. These templates were preincubated with Tax, CREB, p300, and CEM nuclear extract (as indicated), and preinitiation complexes were isolated by gel filtration chromatography. The samples were incubated with [14C]acetyl-CoA, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (5 to 20% polyacrylamide). The sizes of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated. (A) CBP/p300-dependent acetylation of proteins associated with wild-type chromatin templates. Free histones (0.5 μg) were assayed in the absence and presence of p300 as a positive control for acetylation (lanes 1 and 2). Chromatin-assembled templates were assayed in the absence or presence of CEM nuclear extract, as indicated (lanes 3 to 5). Lys-CoA was added to a final concentration of 50 μM (lane 5). (B) CBP/p300-dependent acetylation of proteins associated with tailless chromatin templates. Free histones (2 μg) were assayed as a positive control for acetylation (lane 1). Chromatin-assembled templates were assayed in the absence or presence of CEM nuclear extract and/or Tax/CREB, as indicated (lanes 2 to 6). Lys-CoA was added to a final concentration of 50 μM (lane 4). The Tax/CREB-dependent acetylated protein bands are indicated (*). For this experiment, we used a longer exposure of the image to provide band intensities comparable to those in panel A. (C) Tailless histones are weakly acetylated by p300. Equivalent amounts (2 μg) of wild-type and tailless free histones were incubated in the presence of p300.