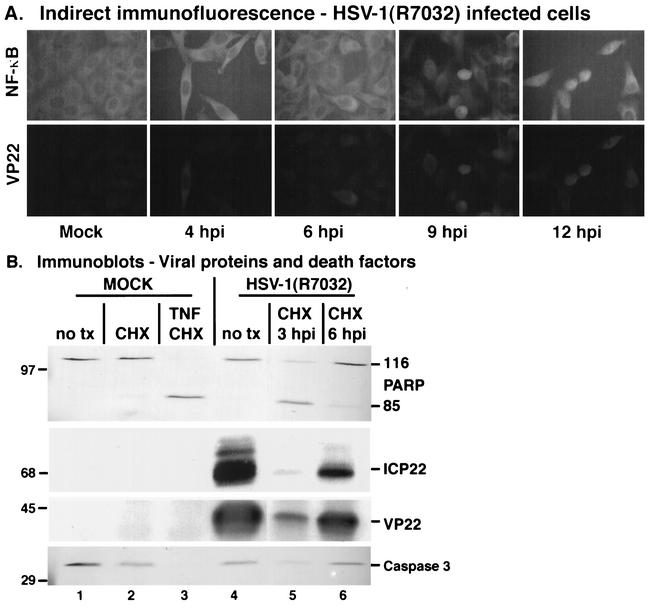
FIG. 6.
(A) Indirect immunofluorescence and immune reactivities indicate that HSV-1(R7032), which contains a deletion in the viral gE, induces and then blocks apoptosis and stimulates NF-κB nuclear translocation during infection. HEp-2 cells were mock infected or infected with HSV-1(R7032) (MOI = 10), prepared for indirect immunofluorescence at 4, 6, 9, and 12 hpi, and double stained with anti-NF-κB or anti-VP22 antibodies as described in Materials and Methods. Magnification, ×85. (B) In a separate analysis, CHX was added to the infected cells at 3 and 6 hpi, while CHX or TNF-α plus CHX was added to mock-infected cells at the time of infection. Infected cell extracts were prepared for immunoblotting of viral proteins and death factors at 18 hpi, and immune reactivities were measured using anti-PARP, anti-ICP22, anti-VP22, and anti-caspase 3 antibodies. Viral and cellular proteins were detected using chemiluminescence and alkaline phosphatase techniques, respectively. 116 and 85 refer to full-length and processed PARP, respectively. “no tx” refers to cells that did not receive CHX or CHX-plus-TNF-α treatments. Locations of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated in the left margins. For clarity, a blank lane was removed between lanes 4 and 5.