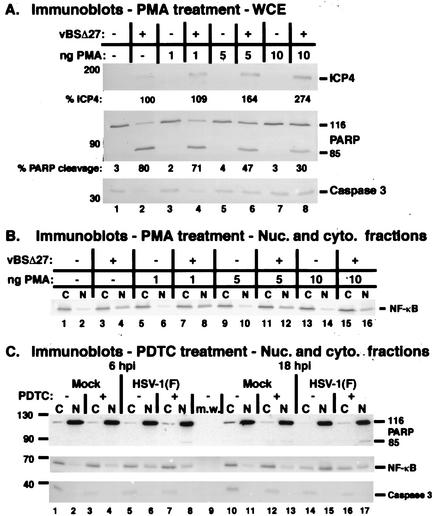
FIG. 8.
Pharmacological modulation of NF-κB. Immune reactivities following PMA (A and B) or PDTC (C) treatments of infected cells. HSV-1(vBSΔ27)-infected (MOI = 10) HEp-2 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PMA for 18 h, and whole-cell extracts (panel A) or cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) extracts (panels B and C) were prepared, separated in denaturing gels, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with anti-NF-κB, anti-ICP4, anti-PARP, and anti-caspase 3 antibodies. Amounts of ICP4 and PARP cleavage were determined using NIH Image software as described in Materials and Methods. HEp-2 cells treated with (+) or without (−) PDTC were mock infected or infected with HSV-1(F) (MOI = 10), and at 6 and 18 hpi cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) extracts were prepared for immunoblotting and probed with anti-PARP, anti-caspase 3, and anti-NF-κB antibodies. Immune reactivities with anti-NF-κB, anti-ICP4, anti-PARP (A), and anti-caspase 3 antibodies were performed using an alkaline phosphatase detection method, while reactivities with the anti-PARP antibody (C) utilized a chemiluminescence technique.