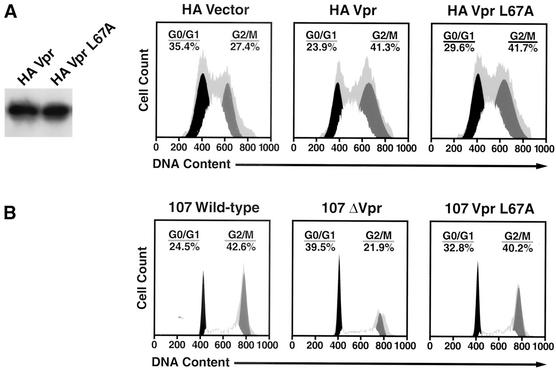
FIG. 2.
The VprL67A mutant induces cell cycle arrest. Cells were analyzed for DNA content, and cell cycle profiles were determined with FlowJo software using the Watson Pragmatic model. Primary data are represented by the gray background. (A) Both wild-type Vpr and the L67A-Vpr export mutant were expressed at comparable levels (left panel) in 293T cells and induced a similar accumulation of cells at the G2/M interface, characterized by a 4N complement of DNA. (B) The Vpr L67A export mutant was introduced as a single amino acid change in the HIV-1 CCR5-dependent 107 proviral backbone. PBMCs were infected for 5 days and stained to assess intracellular p24 production, and the infected lymphocytes (anti-p24gag+) were analyzed for DNA content. Note the significant accumulation of cells paused or arrested at the G2/M phase of the cell cycle for lymphocytes infected with the wild-type and VprL67A mutant viruses, compared with the control 107ΔVpr virus.