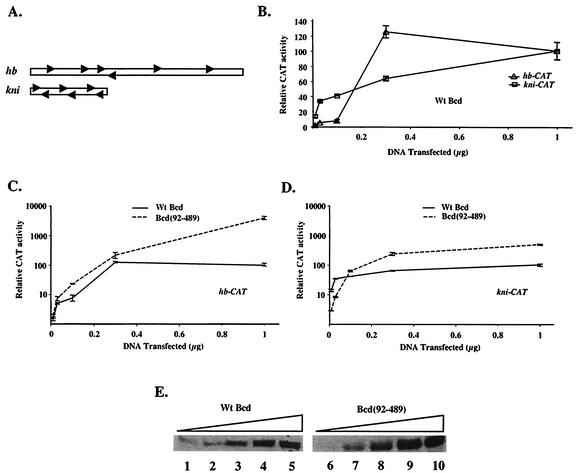
FIG. 1.
The amino-terminal domain of Bcd plays different roles on hb and kni enhancer elements. (A) Schematic diagrams of the 250-bp hb enhancer element and the 64-bp kni enhancer element. The Bcd binding sites are represented by arrows. (B) CAT assay results of S2 cells transfected with hb-CAT and kni-CAT reporter plasmids (1 μg) and increasing amounts of an effector plasmid expressing Bcd. Activities obtained with 1 μg of transfected effector plasmid on each reporter were arbitrarily set to 100 (fold activation was 72 and 74 for hb-CAT and kni-CAT, respectively). (C and D) CAT assay activities (in logarithmic scale) for wild-type Bcd and Bcd(92-489) on hb-CAT (C) and kni-CAT (D) reporters at different concentrations. The activities of wild-type Bcd at 1 μg of transfected effector DNA on each reporters were set to 100. (E) Representative Western blot results detecting Bcd proteins in transfected cells. For the experiments shown in this figure, the amounts of the transfected effector plasmids were 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, and 1 μg. Wt, wild type.