Abstract
Five cases of intrahepatic cholestasis are reported in 4 families in which 7 other children have had the same disease. Cholestasis, beginning before the age of one year, is notable for the absence of lipid retention, evolving by attacks brought on by intercurrent infections with gradual development of fibrosis and fatal cirrhosis before the age of 15. Extrahepatic and interlobular bile ducts are undamaged.
The disease is sometimes accompanied by biliary and pancreatic abnormalities, perhaps due to an abnormality in the biliary acid metabolism.
Full text
PDF
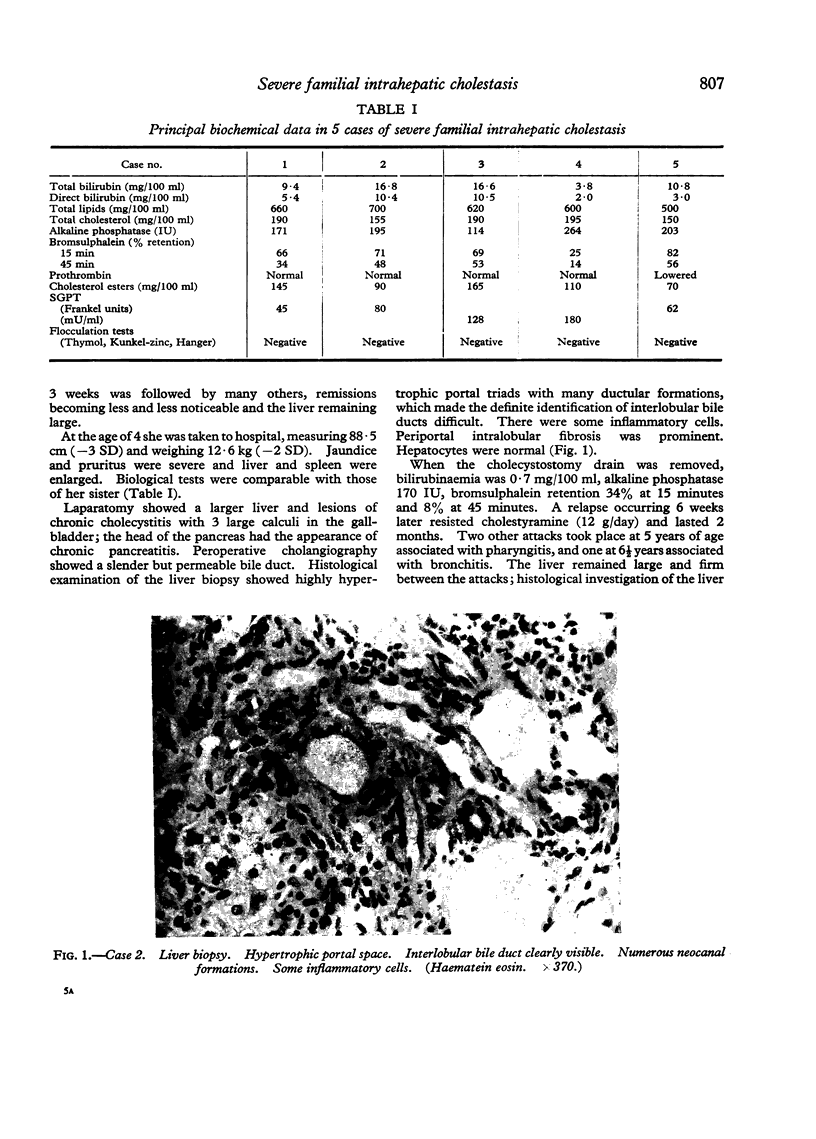





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aagenaes O., van der Hagen C. B., Refsum S. Hereditary recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis from birth. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Dec;43(232):646–657. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.232.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. J., Iber F. L., Ruebner B. H., McKusick V. A. Byler disease. Fatal familial intrahepatic cholestasis in an Amish kindred. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jan;117(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray O. P., Saunders R. A. Familial intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Jun;41(217):320–328. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.217.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSSON K., LUNDH G., STENRAM U., WALLERSTROEM A. PANCREATITIS AND FREE BILE ACIDS. Acta Chir Scand. 1963 Oct;126:338–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka M., Ono T. A case of familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1968 Mar;94(3):293–306. doi: 10.1620/tjem.94.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juberg R. C., Holland-Moritz R. M., Henley K. S., Gonzalez C. F. Familial intrahepatic cholestasis with mental and growth retardation. Pediatrics. 1966 Nov;38(5):819–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linarelli L. G., Williams C. N., Phillips M. J. Byler's disease: fatal intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):484–492. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERSKILL W. H., WALSHE J. M. Benign recurrent intrahepatic "obstructive" jaundice. Lancet. 1959 Oct 31;2(7105):686–690. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. N., Kaye R., Baker L., Hurwitz R., Senior J. R. Progressive familial cholestatic cirrhosis and bile acid metabolism. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):493–500. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaki F. G., Carey J. B., Jr, Hoffbauer F. W., Nwokolo C. Biliary reaction and choledocholithiasis induced in the rat by lithocholic acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 May;69(5):737–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]