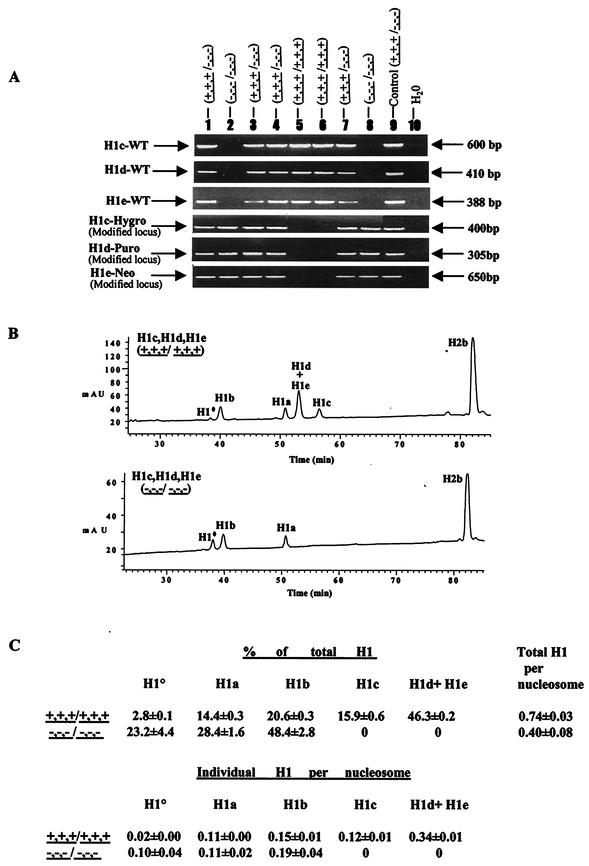
FIG.3.
Analysis of chromatin from H1c H1d H1e triple-null mouse embryos. (A) PCR genotype analysis of E7.5 embryos from intercrosses of H1c+/− H1d+/− H1e+/− mice. Embryo DNA was prepared and analyzed by PCR assays for H1c, H1d, and H1e wild-type (WT) and modified loci as described in Materials and Methods. The deduced genotype of each embryo is indicated above each lane. The positions of the PCR products from the wild-type and modified alleles are indicated. Control reaction mixtures contained tail DNA from an H1c H1d H1e triple-heterozygous mutant mouse. (B) Reverse-phase HPLC analysis of histones in extracts from E10.5 wild-type and homozygous H1c H1d H1e mutant embryos. Approximately 20 μg of total histone extract of chromatin from wild-type (top) and homozygous triple H1c H1d H1e mutant (bottom) E10.5 embryos were fractionated by reverse-phase HPLC. Other details are as in the legend to Fig. 2B. mAU, milli-absorbency units. (C) H1 subtype composition of chromatin from wild-type and H1c−/− H1d−/− H1e−/− E10.5 embryos. Data were calculated from HPLC analyses of wild-type and H1c H1d H1e triple-mutant embryos like that shown in panel B. Other details are as described in the legend to Fig. 2C.