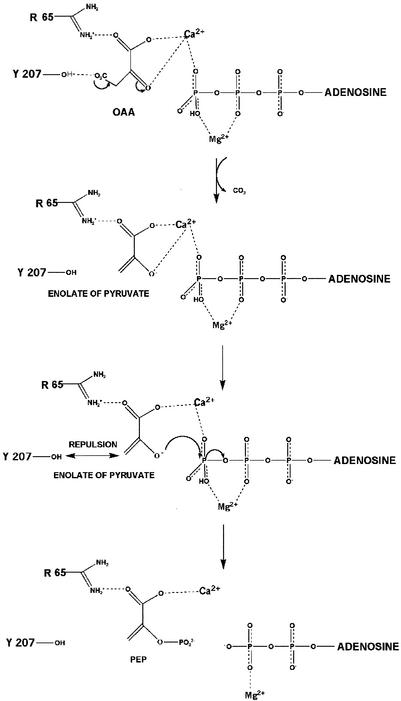
FIG. 9.
Proposed reaction mechanism for the synthesis of PEP by E. coli PCK. Arg65 forms a salt bridge interaction with the carboxylate oxygen atom of OAA. Arg333 further stabilizes the molecule by forming a salt bridge with another carboxylate oxygen atom, thus bridging ATP and OAA. OAA binds in the first coordination sphere of Ca2+, which promotes decarboxylation to form the pyruvate enolate intermediate. Ca2+ electrostatically stabilizes the enolate anion via the carboxylate oxygen and neutralizes the repulsions between the enolate and the γ-phosphoryl group of ATP. Ca2+ serves to orient the two substrates and position the enolate oxygen to attack and displace the γ-phosphoryl group. The hydroxyl group of Tyr207 may also move the substrates closer together by repulsion of the CH2 group of the enolate.