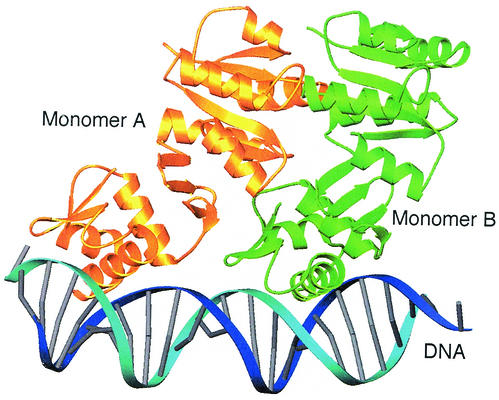
FIG. 4.
Model of DrrB bound to DNA. Shown is a ribbon schematic of the superposition of two full-length DrrB monomers onto the crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of PhoB bound to DNA (1GXP [5]). Monomers A and B are gold and green, respectively, and DNA is blue. There is only one small region of steric conflict between the β3-α4 loop of the regulatory domain of monomer A (residues 80 to 83) and the C-terminal end of helix α1 of the DNA-binding domain of monomer B (residues 160 to 163). Thus the model provides no structural basis for a mechanism of inhibition of DNA binding by the unphosphorylated regulatory domain. This model is not expected to approximate the structure of phosphorylated DrrB bound to DNA. Surfaces of the regulatory domain are presumably altered by phosphorylation, and these alterations would be expected to affect the domain interface, as well as promote specific interactions among regulatory domains within the dimer.