Abstract
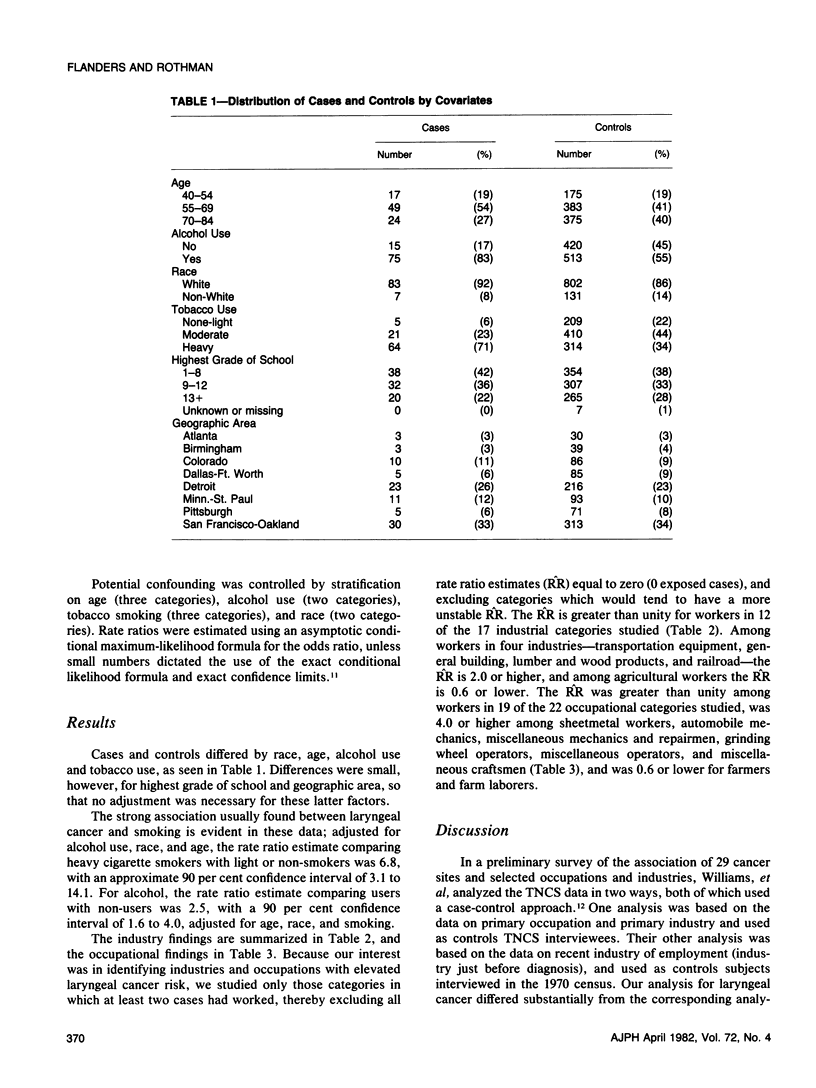
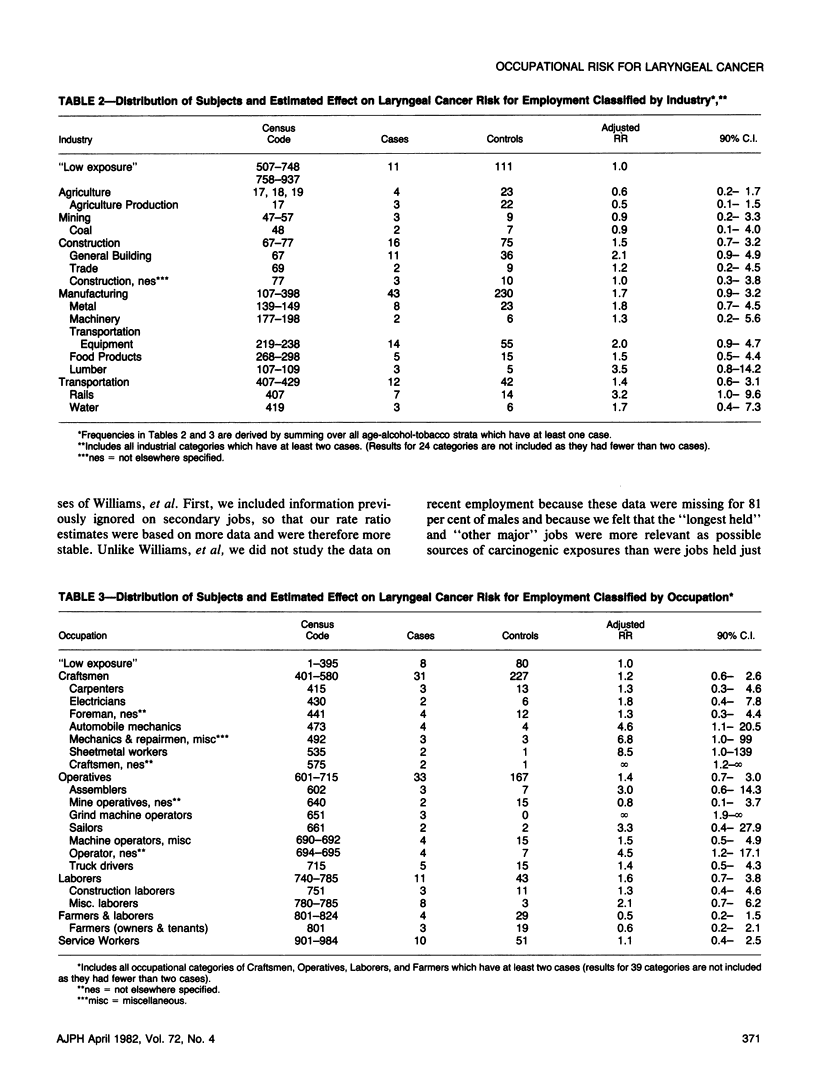
In a case-control analysis, we studied the effects of type of employment on laryngeal cancer risk using the interview data from the Third National Cancer Survey. Effects were measured relative to the risk for those employed in a group of arbitrarily defined industries and occupations with low risk. We excluded females and controlled for age, tobacco use, alcohol use, and race in the analysis. We found ratio estimates above 3.0 for workers in the railroad industry and the lumber industry; and for sheetmetal workers, grinding wheel operators, and automobile mechanics.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CORNFIELD J. A method of estimating comparative rates from clinical data; applications to cancer of the lung, breast, and cervix. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1951 Jun;11(6):1269–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoufle P. Cancer risks associated with employment in the leather and leather products industry. Arch Environ Health. 1979 Jan-Feb;34(1):33–37. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1979.10667364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Shettigara P. T. Occupational asbestos exposure, smoking, and laryngeal carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;271:308–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb23126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J., Cann C. I., Flanders D., Fried M. P. Epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1980;2:195–209. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. R., Stegens N. L., Goldsmith J. R. Associations of cancer site and type with occupation and industry from the Third National Cancer Survey Interview. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Oct;59(4):1147–1185. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.4.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. R., Stegens N. L., Horm J. W. Patient interview study from the Third National Cancer Survey: overview of problems and potentials of these data. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Mar;58(3):519–524. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.3.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf O. Larynxkarzinome bei Naphthalinreinigern. Z Gesamte Hyg. 1978 Oct;24(10):737–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Covey L. S., Mabuchi K., Mushinski M. Environmental factors in cancer of the larynx: a second look. Cancer. 1976 Oct;38(4):1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197610)38:4<1591::aid-cncr2820380425>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


