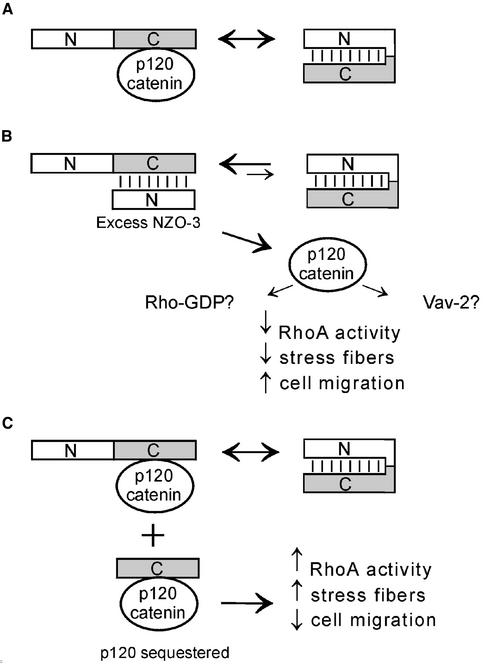
Figure 7.
Hypothetical model for RhoA inhibition in NZO-3/MDCK cells. (A) Parental MDCK cells: The C terminus of endogenous ZO-3 could bind to p120 catenin, or to the N terminus of the same molecule (intramolecular interaction). (B) NZO-3/MDCK cells: Exogenously expressed NZO-3 competes with p120 catenin for binding to the C terminus of endogenous ZO-3. P120 catenin is then available to interact with other proteins such as Vav-2 or Rho-GDP, which can down-regulate RhoA. (C) CZO-3/MDCK cells: p120 catenin could bind to either the C terminus of endogenous ZO-3 or to the CZO-3 construct, thus sequestering it from binding to other effectors and resulting in up-regulation of RhoA.