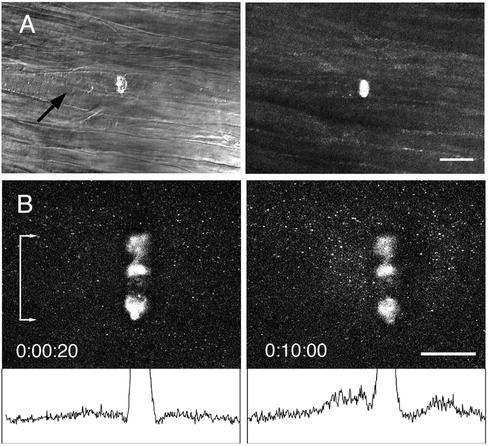
Figure 3.
Multiphoton damage in axons created by a line scan mode with a 25× 0.8 NA water immersion lens. (A) The squid fin nerve contains a bundle of ∼10-μm diameter axons. The multiphoton microscope was focused to a plane ∼50 μm from the surface of the axon bundle, and a line scan at full power created a wound within an axon; axons above and below were undamaged. The transmitted light image shows an accumulation of organelles on the proximal side of the wound after 10 min, indicating blockage of axonal transport. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) The squid giant axon is ∼500 μm in diameter. A line scan wound was made within the axoplasm ∼25 μm from the surface of the axon. The axon had been preincubated with rhodamine 123 to label mitochondria. After 10 min, an accumulation of anterograde and retrograde moving mitochondria was seen at the scar as demonstrated by the difference in intensity profiles (bottom) of a band the full width of the scar (denoted by bar with arrows). Scale bar, 50 μm.