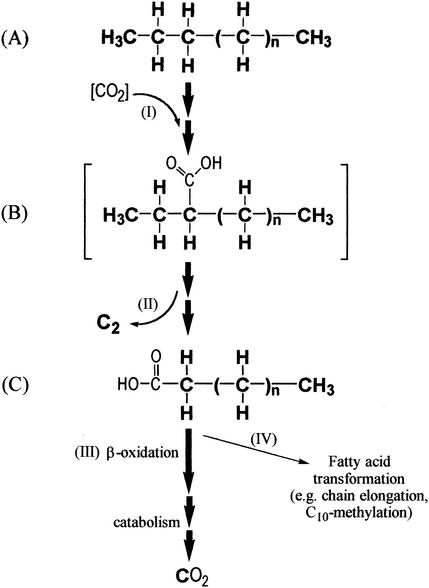
FIG. 5.
Proposed pathway for the oxidation of alkane to fatty acid by strain Hxd3. An alkane (A) is subterminally carboxylated at C-3 (step I) to form an intermediate (B). Two adjacent terminal carbon atoms are then eliminated (step II) to form a fatty acid one carbon shorter than the original alkane (C). This fatty acid can be beta oxidized (step III) and subsequently mineralized to CO2 or undergo transformation, such as chain elongation and C-10 methylation (step IV). Compound B (in brackets) is only a hypothetical intermediate and has not been observed. Atoms originating from the alkane are shown in bold type.