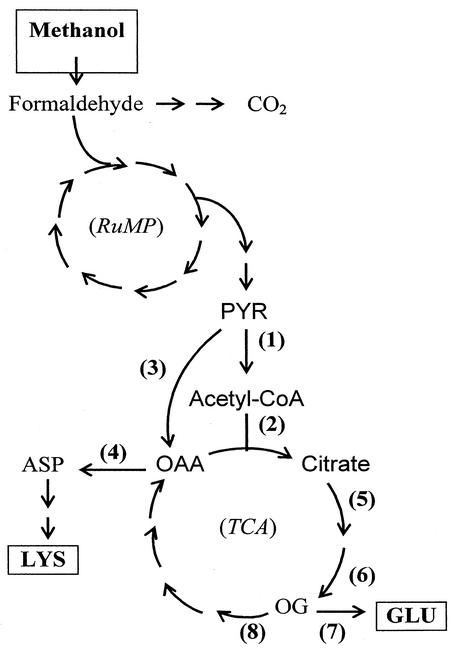
FIG. 1.
Methanol metabolism in B. methanolicus. Methanol is initially oxidized to formaldehyde, which may be dissimilated to CO2 or assimilated to pyruvate via the RuMP pathway. From pyruvate, the carbon flow is split between entering the TCA cycle or conversion to aspartate and its related amino acids. Abbreviations: TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; RuMP, ribulose monophosphate pathway; PYR, pyruvate; ASP, aspartate; OAA, oxaloacetate; OG, 2-oxoglutarate; GLU, glutamate; LYS, l-lysine; CoA, coenzyme A. Enzymes: 1, pyruvate dehydrogenase, PDH; 2, citrate synthase, CS; 3, pyruvate carboxylase, PC; 4, glutamate:oxaloacetate aminotransferase, GOT; 5, aconitase, ACN; 6, isocitrate dehydrogenase, IDH; 7, glutamate synthase, GOGAT; 8, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, OGDC.