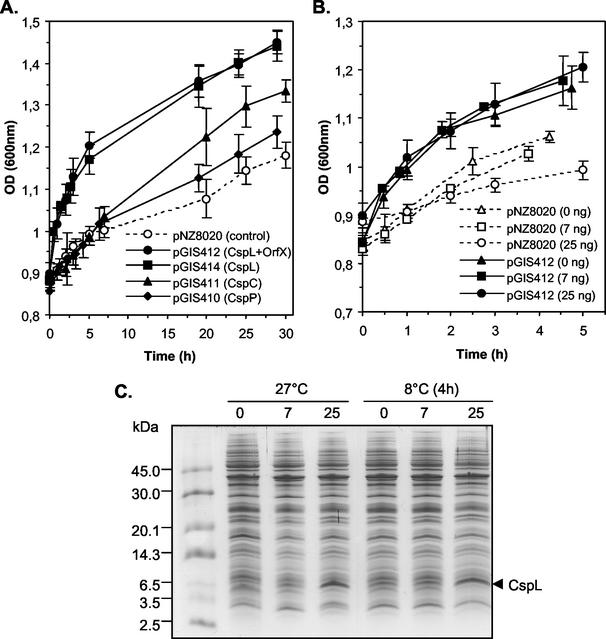
FIG. 2.
Effect of CSP overproduction on growth after cold shock. (A) Cultures of the control strain (dotted line, open circles) and CSP-overproducing strains (solid lines; closed circles, CspL plus OrfX; closed squares, CspL; closed triangles, CspC; closed diamonds, CspP) were inoculated (4%) with overnight precultures and grown at 27°C for 1 h before nisin addition (25 ng ml−1). Exponentially growing cultures (OD600 of 0.85) were transferred from 27 to 8°C and growth was monitored for 30 h. Error bars represent standard deviations from the means (n = 3). (B) Effect of the increase in nisin concentration on growth after cold shock of the CspL-overproducing strain. Cultures of the control strain (pNZ8020; dotted lines and open symbols) and the CspL-overproducing strain (pGIS412; solid lines and closed symbols) were inoculated (4%) with overnight precultures and grown at 27°C for 1 h before nisin addition. The nisin concentrations used for induction were 0 ng ml−1 (triangles), 7 ng ml−1 (squares), and 25 ng ml−1 (circles). Exponentially growing cultures (OD600 of 0.85) were transferred from 27 to 8°C and growth was monitored for 4 to 5 h. The data were obtained from three independent cultures for both the controls and the CspL-overproducing strains. Error bars represent standard deviations from the means (n = 3). (C) Coomassie brilliant blue-stained gel after Tricine-SDS-PAGE showing the dose-dependent nisin induction of CspL synthesis before and after cold shock. Equal amounts of total proteins (13 μg) of cell extracts from the CspL-overproducing strain (pGIS412) grown at 27°C and downshifted for 4 h at 8°C (as indicated on the top of respective lanes) were subjected to electrophoresis. The nisin concentrations used for induction were 0, 7, and 25 ng ml−1 (as indicated on the top of respective lanes). The molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) are indicated to the left, and the bands corresponding to CspL are indicated by an arrow.