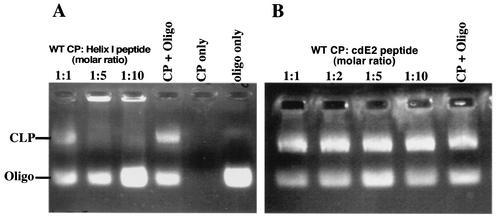
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of wild-type CLP assembly in vitro with peptides corresponding to helix I and the cytoplasmic domain of E2. (A) In vitro assembly with the helix I peptide. A 0.8% agarose gel stained for nucleic acid with ethidium bromide shows in vitro-assembled CLPs and unincorporated oligonucleotides (Oligo). E. coli-expressed wild-type (WT) CP and helix I peptide were incubated together at the indicated molar ratios and allowed to equilibrate at room temperature. The samples were then mixed with a 48-mer oligonucleotide and incubated at room temperature for 15 to 30 min. CLP assembly was assayed by agarose gel analysis as previously described (37). The data show that increasing amounts of helix I peptide (left to right) inhibit wild-type CLP assembly. (B) In vitro assembly with a peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 24 residues of the cytoplasmic domain of E2 (cdE2) of SINV. The data show that increasing amounts of the cdE2 peptide (left to right) do not inhibit wild-type CLP assembly.