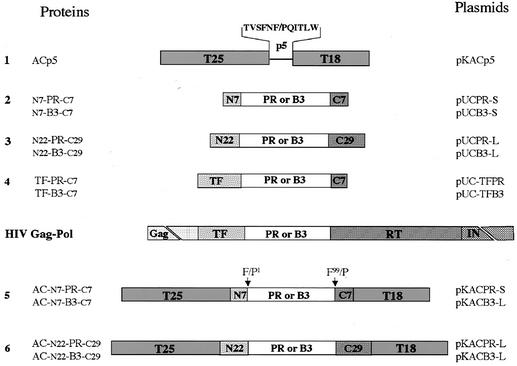
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of AC proteins and HIV PRs used in this work. (Panel 1) In ACp5 protein, a specific proteolytic site of HIV PR, named p5 (amino acid sequence in one-letter code), was inserted in frame between the two complementary fragments of the catalytic domain of B. pertussis AC, T25 (residues 1 to 224) and T18 (residues 225 to 400), represented as grey rectangles. (Panels 2 to 4) Wild-type HIV PR and/or B3 variant (mature polypeptide of 99) are represented as white rectangles. The dotted rectangles (N7, N22, and TF) represent the various flanking segments deriving from the TF protein coding regions of 7, 22, and 68 residues (full TF protein), respectively. The hatched rectangles represent the RT-derived polypeptides (C7 or C29). HIV Gag-Pol represents the schematic organization of the HIV polyprotein precursor Gag-Pol. (Panels 5 and 6) Wild type or B3 variant of HIV PR, flanked by short (N7/C7) or long (N22/C29) flanking sequences, were inserted in frame between T25 and T18 fragments of AC.