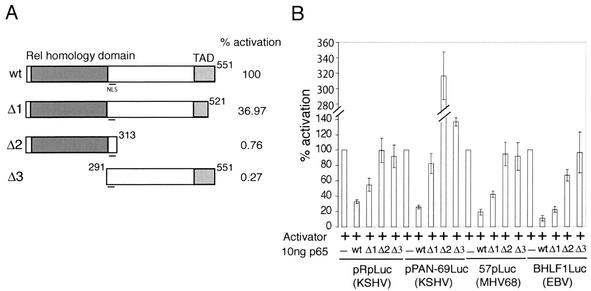
FIG. 5.
Both the activation domain and DNA binding domain of p65 are required for inhibition of MHV68 lytic gene expression. (A) Diagram of pFLAGp65 deletion mutants used in panel B and Fig. 6. The N-terminal DNA binding/dimerization (Rel homology) domain and C-terminal activation domain (TAD) are indicated. Mutants were tested for transactivation by transient transfection into 293T cells with a reporter bearing five consensus NF-κB binding sites upstream of firefly luciferase (pNF-κBLuc). The percentage of activation represents the average results comparing 5, 10, and 50 ng of each pFLAGp65 construct in three separate experiments. (B) Transient transfection of 293T cells as described for Fig. 1B. Cells were transfected with RTA or RTA and Zebra (+) and 10 ng of wild type (wt), Δ1, or Δ2 pFLAGp65.