FIG. 2.
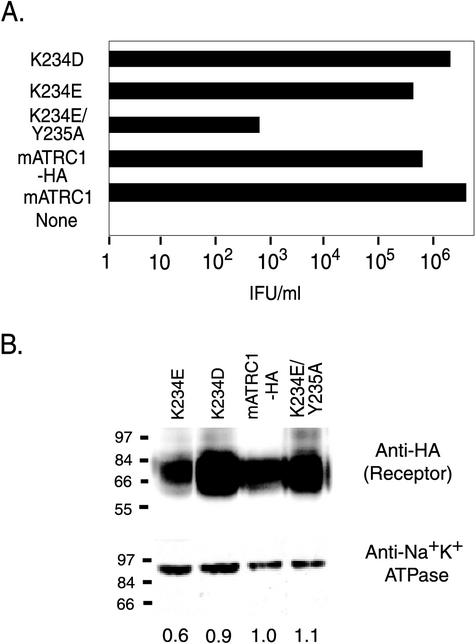
Lysine 234 is critical to ecotropic MLV infection. (A) HEK 293 cells stably expressing HA1 epitope-tagged receptors were exposed to 10-fold serial dilutions of high-titer ecotropic MLV-pseudotyped BAG virus stock, and infectious titers were determined from the end point dilution (n = 4). None, parental HEK 293 cells lacking ecotropic MLV receptor; mATRC1, untagged wild-type receptor; mATRC1-HA, HA-tagged wild-type receptor; K234E/Y235A, HA-tagged mutant receptor with combined replacement of lysine 234 with glutamate and tyrosine 235 with alanine; K234E and K234D, HA-tagged mutant receptors with single replacements of lysine 234 with glutamate and aspartate, respectively. IFU, infection-forming units. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the surface expression of mutant receptors. Surface proteins on live HEK 293 cells stably expressing HA-tagged mATRC1 or mutant receptors were labeled with biotin by using a membrane-impermeant biotinylation reagent, and then cells were lysed and equal masses of each lysate were incubated with avidin-agarose beads to affinity purify plasma membrane proteins as described in the text. (Top) Half of the total purified surface membrane proteins were applied to each lane and immunoblotted to mouse anti-HA1 monoclonal antibody HA11. Detection was performed with goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G conjugated to HRP and a chemiluminescent substrate for HRP. (Bottom) The other half of total purified surface membrane proteins were immunoblotted to anti-Na+K+ATPase as a control to normalize for efficiency of recovery of total surface proteins during affinity purification. The values shown underneath the lanes represent the average relative surface expression levels of mutant receptors compared to that of mATRC1 from two independent experiments calculated from the scanned images with ImageQuant software.