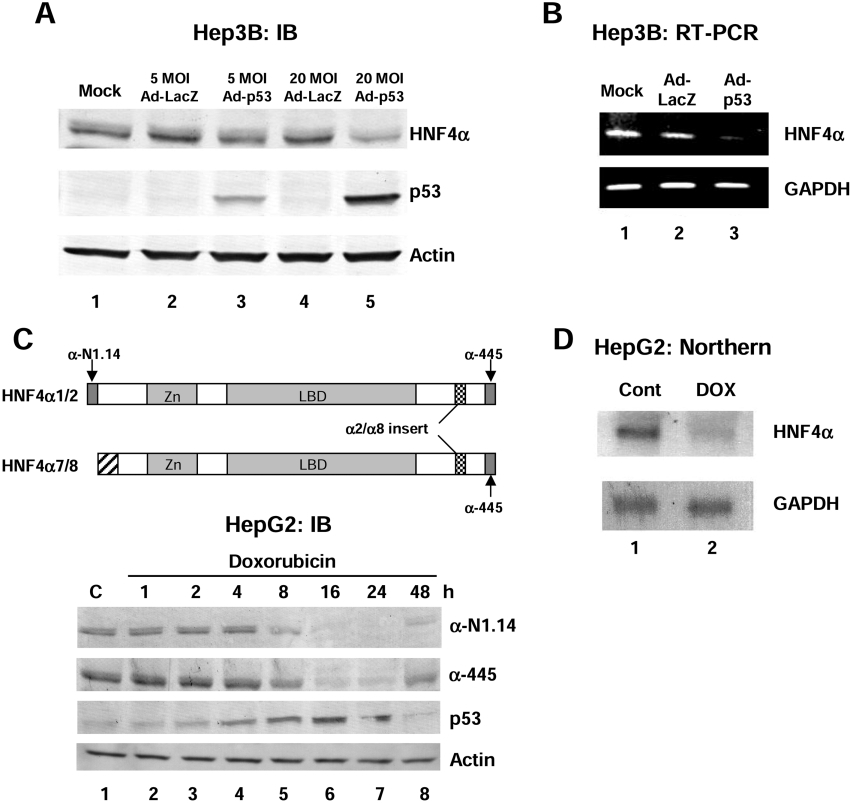
Figure 1. Over expression of wild-type p53 in human liver cancer cell lines results in a decrease in HNF4α1/2 protein and mRNA levels.
(A) IB (immunoblot) analysis using the colour reaction of whole cell extracts from Hep3B cells (60 μg of protein per lane) harvested 48 h after infection of recombinant adenovirus expressing wild-type p53 (Ad-p53) using antibodies against HNF4α (α-445), p53 (DO-1) and β-actin as indicated. Recombinant adenovirus expressing LacZ was used as a control (Ad-LacZ). Similar results were observed using the αN1.14 antibody [results not shown, see (C) below]. Mock, media only added. (B) RT-PCR analysis using HNF4α or GAPDH primers. The template was 0.5 μg of total RNA from Hep3B cells 36 h after infection with Ad-p53 or Ad-LacZ. (C) Upper panel: schematic diagram of HNF4α1/2 and HNF4α7/8 isoforms and the antibodies that recognize them. α-445 recognizes all four isoforms. α-N1.14 recognizes only the isoforms from the P1 promoter (HNF4α1 and HNF4α2). Lower panel: IB (immunoblot) analysis using the colour reaction of whole cell extracts from HepG2 cells (50 μg of total protein per lane) harvested after exposure to doxorubicin (0.5 μg/ml) for the times indicated using antibodies against HNF4α (α-445 and α-N1.14), p53 (DO-1) and β-actin as indicated. C, control (not treated). (D) Northern blot analysis with HNF4α or GAPDH cDNA probes and 8 μg of total RNA from HepG2 cells treated with 0.5 μg/ml doxorubicin (DOX) for 24 h or untreated (Cont).