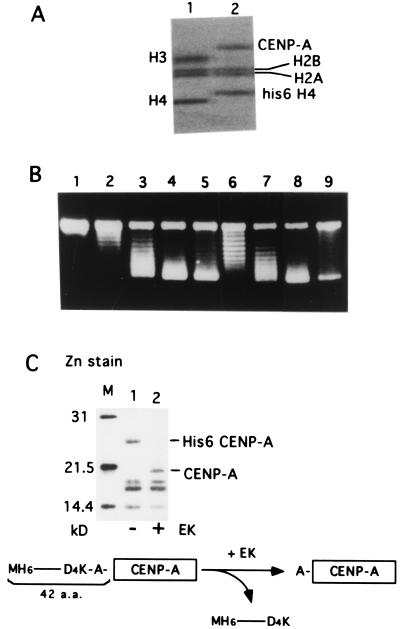
Figure 2.
Topo I analysis using the recombinant CENP-A purified under native condition. (A) 4–20% SDS/PAGE of native core histones (0.24 μg, lane 1) and native CENP-A/core histones (0.12 μg, lane 2). The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue after electrophoresis. (B) Topo I analysis of the native CENP-A/core histones (lanes 6–9) compared with the native core histones (lanes 2–5). Nucleosome reconstitution was carried out by using the relaxed form of pUC-α11mer DNA (100 ng) and NAP-1 as described in Methods. Supercoil ladders were detected with ethidium bromide staining after agarose gel electrophoresis. The amounts of the native core histones were 0 ng (lane 1), 72 ng (lane 2), 98 ng (lane 3), 120 ng (lane 4), and 180 ng (lane 5), and the amounts of His6CENP-A/core histones were 63 ng (lane 6), 100 ng (lane7), 126 ng (lane 8), and 250 ng (lane 9). (C) EK digestion of the complex removes the histidine tag at the N terminus of CENP-A. Mononucleosomes were isolated by glycerol density-gradient sedimentation after MNase digestion of the reconstituted complexes formed from His6CENP-A/core histones and DNA with (lane 2) or without (lane 1) EK digestion and separated by 15% SDS/PAGE. The gel was stained with Zn. The primary structure of the N terminus of His6CENP-A is shown at the bottom.