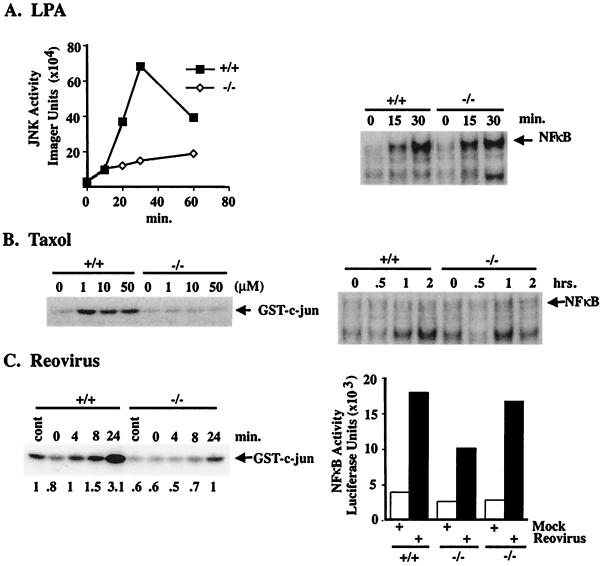
Figure 4.
JNK and NF-κB regulation in MEKK1−/− and wild-type ES cells. (A) Cells were removed from serum for 5 h and then challenged with 10 μM LPA for the indicated times. JNK activity was assayed by using glutathione S-transferase (GST)-c-Jun as substrate by in vitro kinase assay. NF-κB was assayed by EMSA. (B) Cells were challenged with different concentrations of taxol for 30 min for JNK assay and with 10 μM taxol for the indicated times for NF-κB assay. (C) Cells were infected with the Abney strain of reovirus (multiplicity of infection = 4) or mock infected in the absence of virus. At the indicated times after infection, cells were assayed for JNK or NK-κB activity. JNK activity was quantitated by PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics) analysis, with control activity given a value of 1.0 for the MEKK1+/+ cells (shown as numbers under the autoradiograph). NF-κB activity was assayed by electroporation of an NF-κB-regulated luciferase reporter gene 24 h before virus infection. Two independent MEKK1−/− ES clones are shown for the NF-κB assay after reovirus infection. Each experiment is representative of two to four independent experiments for each stimulus.