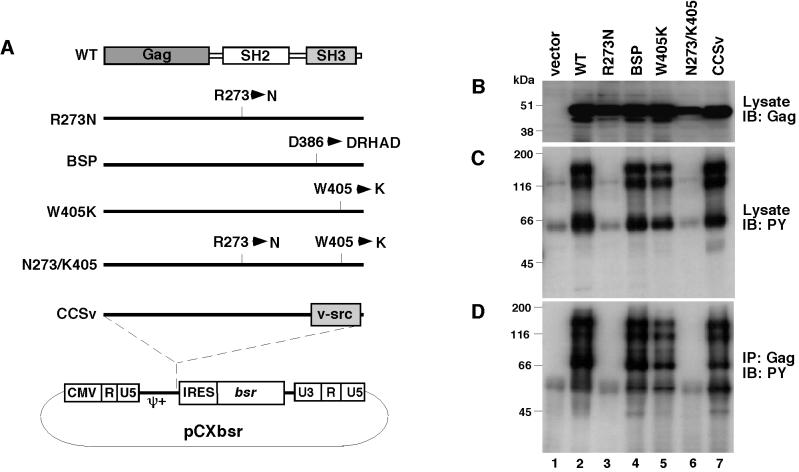
Figure 1.
Characterization of CEF expressing v-Crk mutants. (A) Schematic structure of the v-Crk mutants used in this study. Amino acid changes in each mutant are indicated in the single-letter amino acid code. Detailed descriptions about each mutant are given in Materials and Methods. pCXbsr is a Moloney MuLV-based retroviral vector. CMV, human cytomegalovirus; ψ+, extended retroviral packaging signal; IRES, internal ribose entry site; bsr, Blasticidin S resistance gene. (B) Expression of v-Crk mutants. v-Crk proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-Gag antibody 3C2 by using total cell lysates from CEF expressing v-Crk mutants as indicated above each lane. (C) Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in CEF expressing v-Crk mutants. Tyrosine phosphorylated proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine mouse monoclonal antibody 4G10 by using total cell lysates from CEF expressing v-Crk mutants as indicated above each lane. (D) Association of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins with v-Crk mutants. Tyrosine phosphorylated proteins associated with v-Crk mutants were detected by immunoprecipitation with the anti-Gag antibody 3C2 followed by immunoblotting with the anti-phosphotyrosine rabbit polyclonal antibody.