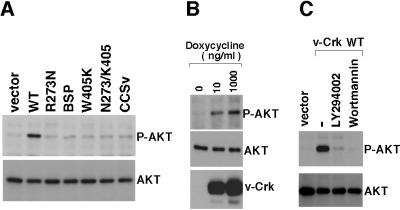
Figure 4.
Analysis of v-Crk-induced AKT phosphorylation. (A) AKT phosphorylation in CEF expressing v-Crk mutants. Total cell lysates from CEF expressing v-Crk mutants (indicated above each lane) were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibody specific for the phosphorylated form of AKT (P-AKT) (Upper) or with antibody to AKT that reacts with AKT irrespective of phosphorylation state (Lower). (B) AKT phosphorylation in an inducible v-Crk expression system. CEF dually infected with CXneo/TR-2 and CXbsrR(TO/v-Crk WT) were cultured with the indicated concentrations of doxycycline for 24 h. Total cell lysates from these cells then were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibody specific for the phosphorylated form of AKT (P-AKT) (Top), with antibody to AKT that reacts with AKT irrespective of phosphorylation state (Middle), or with anti-Gag antibody (Bottom). (C) Effects of PI3K inhibitors. CEF expressing WT v-Crk were treated for 2 h with LY294002 (Calbiochem) at 10 μM, wortmannin (Calbiochem) at 200 nM, or with the solvent DMSO (−). Then, total cell lysates from these cells as well as from vector-transduced cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibody specific for the phosphorylated form of AKT (P-AKT) (Upper) or with antibody to AKT that reacts with AKT irrespective of phosphorylation state (Lower)