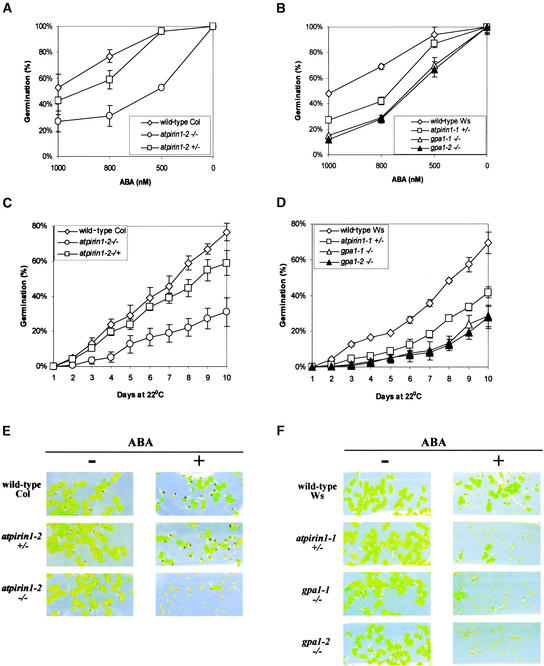
Figure 5.
Seed Germination and Early Seedling Development of atpirin1 and gpa1 Mutants Are Hypersensitive to ABA.
Matched seed lots on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (1962) agarose medium supplemented with ABA were stratified for 48 h at 4°C before being placed at 22°C under continuous white light for germination. Heterozygous and homozygous mutants are indicated by +/− and −/−, respectively, next to the corresponding mutant genotype.
(A) Germination of wild-type Col seeds and atpirin1-2 mutant seeds in the presence of the indicated concentrations of ABA at day 10 after stratification.
(B) Germination of wild-type Ws seeds and atpirin1-1, gpa1-1, and gpa1-2 mutant seeds in the presence of the indicated concentrations of ABA at day 10 after stratification.
(C) Germination of wild-type Col seeds and atpirin1-2 mutant seeds in the presence of 800 nM ABA over time (days after stratification).
(D) Germination of wild-type Ws seeds and atpirin1-1, gpa1-1, and gpa1-2 mutant seeds in the presence of 800 nM ABA over time (days after stratification).
Values shown in (A) to (D) are mean percentages of germination from three independent experimental replicates (each replicate included 70 to 150 seeds per line) with standard errors.
(E) Early seedling development of atpirin1-2 mutants is inhibited by ABA. No ABA (−) or 500 nM ABA (+) was added to the growth medium in phytatrays. Note that >50% of the mutant seeds shown are germinated as judged by radicle emergence (cf. with [A]).
(F) Early seedling development of atpirin1-1, gpa1-1, and gpa1-2 mutants is inhibited by ABA. No ABA (−) or 800 nM ABA (+) was added to the growth medium in phytatrays. Note that ∼30 to 40% of the mutant seeds shown are germinated as judged by radicle emergence (cf. with [D]).
Photographs for (E) and (F) were taken on day 10.