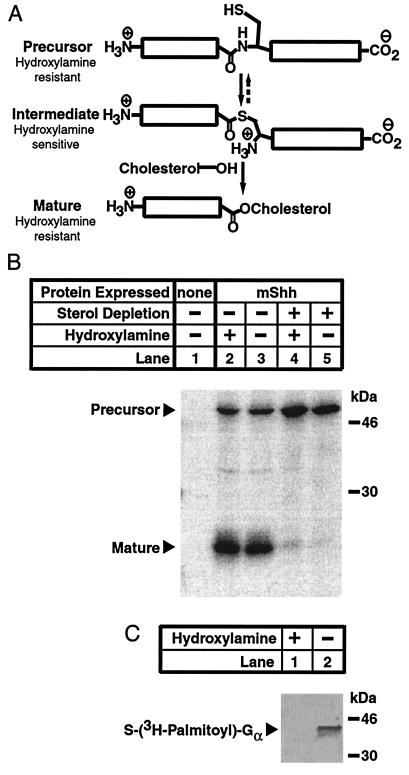
Figure 4.
Resistance of mShh precursor to neutral hydroxylamine. (A) Schematic representation of the chemical reactions carried out during mShh autoprocessing. First, mShh precursor converts to a semistable thioester intermediate by attack of the side chain thiol of Cys-199 on the carboxamide of the immediately amino-terminal Gly. Next, the intermediate form of mShh is converted to the cholesterol ester mature form by the attack of cholesterol on the thioester. Amides and esters are resistant to cleavage by neutral hydroxylamine whereas thioesters are labile to such cleavage. (B) Resistance of mShh precursor to neutral hydoxylamine. CHO-7 cells, where indicated stably expressing mShh, were grown overnight in medium A. One hour before metabolic labeling, the medium was replaced, as indicated, with sterol-depriving medium. Cells were labeled for 30 min with 35S-labeled Met followed by a 15-min chase. Recombinant mShh was immunoprecipitated from detergent lysates with mouse α-FLAG(M2)⋅agarose (see Materials and Methods). Before elution from the beads, immunoprecipitated mShh proteins were treated, as indicated, with either 1 M Tris·HCl (pH 7.4) or 1 M hydroxylamine (pH 7.4) for 30 min at 37°C. The resulting protein mixtures were eluted as described and subjected to SDS/PAGE (12% gel). (C) Lability of the palmitate thioester of G protein α to neutral hydroxylamine. Control immunoprecipitates were prepared from cells treated as described above without radiolabeling. Immediately before hydroxylamine treatment, the samples were treated with in vitro-translated G protein α that had been labeled with tritiated palmitate (24,000 cpm per sample). Before elution from the beads, these samples were then subjected, as indicated, to treatment with either 1 M Tris·HCl (pH 7.4) or 1 M hydroxylamine (pH 7.4) for 30 min at 37°C. The resulting protein mixtures were eluted from the beads, subjected to SDS/PAGE (12% gel), and transferred electrophoretically to an Immobilon P membrane.