Figure 1.
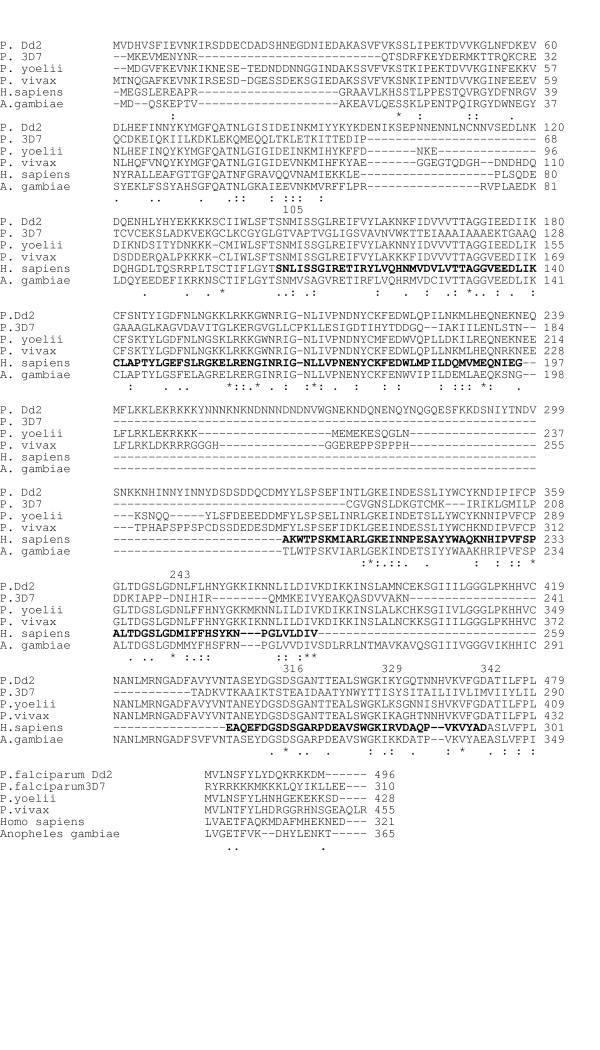
Amino acid alignment between a putative DHS protein from P. vivax and two different P. falciparum strains, the rodent malaria parasite P. yoelii, human and the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Numbering refers to DHS in the two P. falciparum species. Lane 1: P. falciparum strain Dd2 (accession number AF290977); lane 2: P. falciparum strain 3D7 (accession number NC_004317); lane 3: P. yoelii (XM-724232); lane 4: P. vivax (AJ549098) ; lane 5: human (U26266), lane 6: Anopheles gambiae (XM-316567). Gaps (-) were introduced to obtain maximum alignment. Arterisks label amino acid identities, colons (:) and dots (.) label amino acid similarities. The spermidine binding site (243–329 refering to human DHS numbering) is marked by bold amino acids. The NAD binding site from serine105 to aspartic acid 342 is marked in bold letters. The active center of the DHS protein from glutamine 324 to lysine 329 is bolded black.
