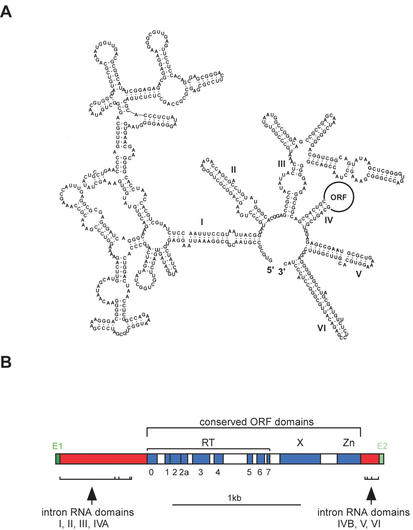
Figure 1.
Structure of mobile group II introns. (A) RNA secondary structure. An example RNA secondary structure is shown for Novosphingobium aromaticivorans I1 (GenBank accession # AF079317), showing the six structural domains. When the intron encodes an ORF, it is looped out of domain IV. (B) Intron-encoded ORF structure. A typical ORF structure is shown. The largest domain (RT) contains the seven subdomains common to all reverse transcriptases (0–7). Additional domains are domain X, which contributes a splicing, or maturase, function, and the Zn domain, which has an endonuclease activity utilized in mobility. The Zn domain is absent from many bacterial intron ORFs. The six RNA structural domains surround the ORF and are flanked by exon sequences (E1 and E2).