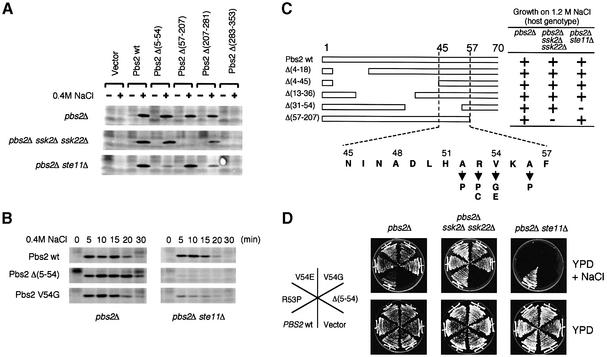
Fig. 2. (A and B) Effect of Pbs2 N-terminal deletions on Hog1 activation. (A) Centromeric plasmids carrying either no insert (Vector), wild-type PBS2 (wt) or the indicated pbs2 deletion mutations were introduced individually into TM260 (pbs2Δ), TM280 (pbs2Δ ssk2Δ ssk22Δ), or KT503 (pbs2Δ ste11Δ). Cells were collected before (–) and 5 min after (+) addition of 0.4 M NaCl, and Hog1 activation was examined by immunoblotting the total lysate with an anti-phosho-p38 antibody, which cross-reacts with activated Hog1. (B) Further characterization of the effect of pbs2Δ(5–54) and pbs2V54G mutations on Hog1 activation. Plasmids containing either the wild-type PBS2, or the pbs2Δ(5–54) or pbs2V54G mutants were introduced into TM260 or KT503. Cells were collected at the indicated times after addition of 0.4 M NaCl, and Hog1 activation was examined as in (A). (C and D) Identification of the sequence within the Pbs2 RSD-I region that is required for signal transduction from the SLNI branch. (C) Deletion analysis of the Pbs2 RSD-I region. The effect of a series of short deletions in the RSD-1 region on the ability of Pbs2 to complement osmosensitivity was investigated essentially as described in Figure 1B. The amino acid sequence of the minimally essential region, as well as the isolated missense mutations that showed the same phenotype as Δ(5–54), are shown at the bottom. (D) Osmosensitivity phenotypes of several mutants in RSD-I. the osmosensitivity of various RSD-I mutants was tested in three host strains, TM260, TM280 and KT503, as described in Figure 1C.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.