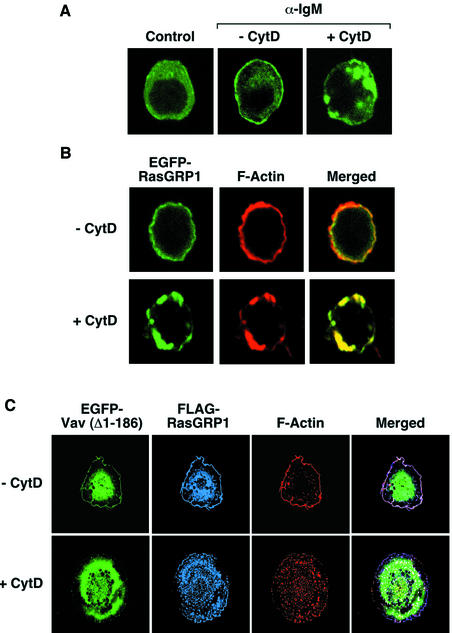
Fig. 5. (A and B) Effect of cytochalasin D in the subcellular localization of RasGRP1 in wild-type DT40 cells. Cells expressing EGFP–RasGRP1 were incubated with cytochalasin D (10 µM) for 2 h and either left non-stimulated (A, first panel) or stimulated (A and B) with anti-IgM antibodies (10 µg/ml) for 5 min. Cells were then fixed, stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (B) and subjected to microscope analysis. Images show the areas of localization of EGFP–RasGRP1 and F-actin in green (A and B) and red (B), respectively. The areas of overlap between those two proteins are shown in yellow (B). (C) Effect of cytochalasin D in the subcellular localization of RasGRP1 in COS1 cells. Cells expressing FLAG-RasGRP1 and EGFP-Vav (Δ1–186) were either left untreated (upper panels) or were treated with cytochalasin D (2 µM) for 30 min (lower panels). After this step, cells were fixed, incubated with rabbit anti-FLAG antibodies followed by Cy5-labeled antibodies to rabbit IgGs, stained with rhodamine-phalloidin and analyzed by immunofluorescence analysis. Images show the localization of EGFP-Vav (Δ1–186), FLAG-RasGRP1 and F-actin in green, blue and red, respectively. The areas of overlap between RasGRP1 and F-actin are shown in purple (right panels).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.