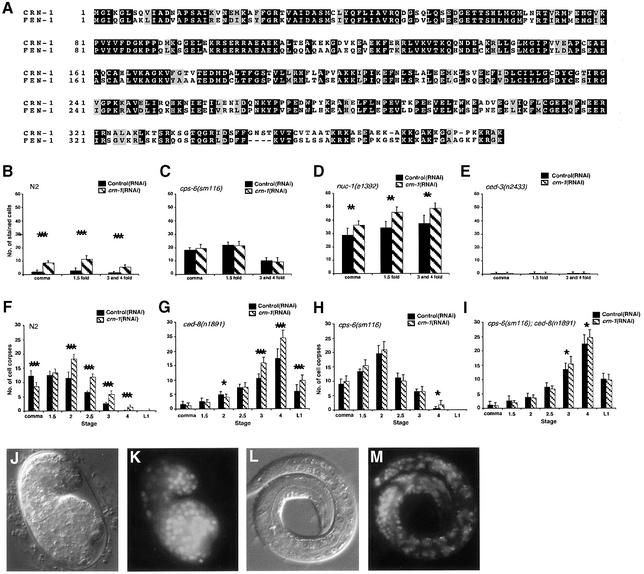
Fig. 1. crn-1 encodes a FEN-1-like nuclear protein important for C.elegans apoptosis. (A) Alignment of CRN-1 and human FEN-1. Black shaded residues are identical and gray shaded residues are similar in two proteins. (B–E) TUNEL assays. N2 (B), cps-6(sm116) (C), nuc-1(e1392) (D) and ced-3(n2433) (E) animals were treated with control(RNAi) (filled bars) or crn-1(RNAi) (hatched bars) and their progeny were stained with TUNEL. The stages of embryos examined were comma, 1.5-fold and 3- and 4-fold. The y axis represents the mean number of TUNEL-positive cells present in the embryos (at least 12 embryos were scored at each stage). (F–I) Time course analysis of embryonic cell corpses. N2 (F), ced-8(n1891) (G), cps-6(sm116) (H), cps-6(sm116); ced-8(n1891) (I) animals were treated with control(RNAi) or crn-1(RNAi) and their progeny were scored for cell corpses in comma, 1.5-, 2-, 2.5-, 3-, 4-fold stage embryos and early L1 larvae. At least 15 animals were scored for each stage. (B to I) Data derived from control and crn-1(RNAi) treatment at the same stage were compared using unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.002; ***P < 0.0001. All other points had P values > 0.05. Error bars indicate one standard deviation (SD). (J–M) Nuclear localization of CRN-1. Nomarski (J and L) and GFP fluorescent (K and M) images of a 1.5-fold stage transgenic embryo and a L1 transgenic larva are shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.