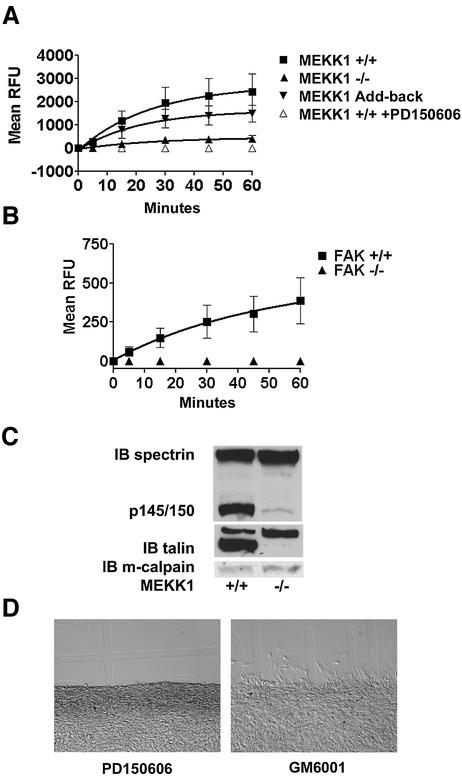
Fig. 6. MEKK1-deficient fibroblasts show reduced calpain activity, and calpain inhibition mimics MEKK1 deficiency. In vivo calpain activity was assessed in fibroblasts using the cell-permeable, fluorescent calpain substrate SLLVY-AMC (A and B) and by anti-spectrin or anti-talin immunoblotting (C). (A) MEKK1+/+ cells in the presence and absence of the calpain inhibitor PD150606 (50 µM), MEKK1–/– and MEKK1 add-back cells were used for measurement of calpain activity. (B) FAK+/+ and FAK–/– cells were used to measure calpain activity as in (A). (C) The anti-spectrin and anti-talin immunoblots were stripped and reprobed with anti-m-calpain antibodies to verify protein levels. The immunoblots are representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) Wild-type fibroblasts grown to confluency on coverslips were pre-treated for 1 h with 50 µM PD150606 (left panel) or 2 µM GM6001, a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (right panel), and then analyzed for migration using the in vitro wound healing assay following a razor swipe in the continuous presence of inhibitor. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments for each set of experiments in (A–D).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.