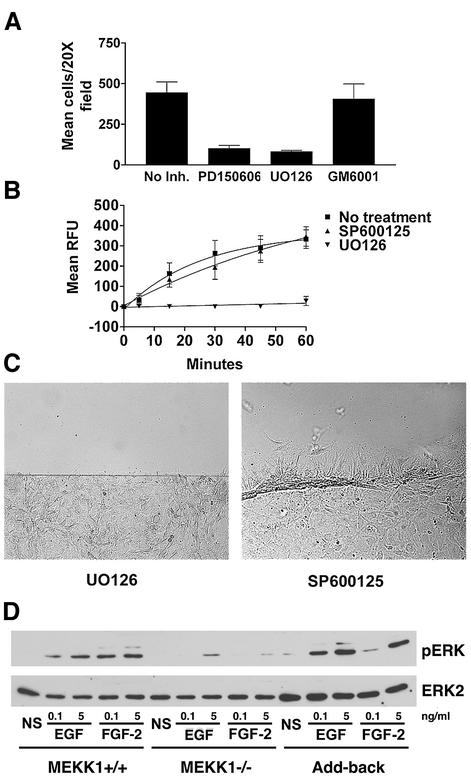
Fig. 7. Fibroblast migration and calpain activity are dependent on MEK, but not JNK activity. (A) Wild-type fibroblasts were loaded into Transwell migration chambers (105 cells/well) and allowed to migrate for 5 h, using 5% serum as a chemotactic agent. Calpain inhibitor PD150606 (50 µM), MEK inhibitor UO126 (10 µM) or matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor GM6001 (2 µM) were added to both the upper and lower chambers of the designated wells. (B) Wild-type fibroblasts were pre-incubated for 1 h with JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 µM) or MEK inhibitor UO126 (10 µM), and calpain activity was assessed by SLLVY-AMC cleavage, and compared with that of non-treated cells. The results of both (A) and (B) are the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. (C) Wild-type fibroblasts were pre-incubated with 10 µM SP600125 or 10 µM UO126 for 1 h and then analyzed for migration using the in vitro wound healing assay in the continuous presence of inhibitor. (D) Serum-starved wild-type, MEKK1–/– or MEKK1 add-back fibroblasts were treated with EGF or FGF-2 for 10 min and then lysed. ERK1/2 activation was then assessed by phospho-ERK immunoblotting. The membrane was then stripped and the total ERK2 level determined by ERK2 immunoblotting. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. NS, no stimulus.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.