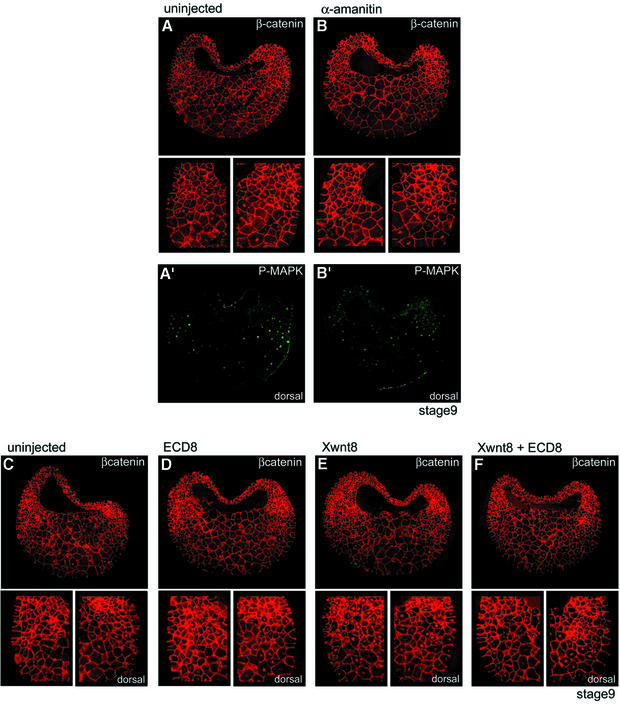
Fig. 6. Nuclear β-catenin in the marginal zone is maternal and independent of Wnt ligands. (A and B) Double staining for β-catenin (A and B) and P-MAPK (A′ and B′) of cryosections from (A) control embryos or (B) embryos injected with α-amanitin (stage 9, 4 × 50 pg). Small panels show enlargements of β-catenin staining in the ventral and dorsal marginal zone. α-amanitin strongly reduced the P-MAPK signal but had no effect on nuclear β-catenin, neither on the dorsal nor on the ventral side. (C–F) β-catenin staining for (C) control embryos or for embryos injected with mRNA coding for (D) the extracellular domain of Xenopus Frizzled 8 (ECD8, 4 × 500 pg), (E) Xwnt8 (4 × 10 pg) or (F) ECD8 and Xwnt8. Xwnt8 strongly increased nuclear β-catenin on the ventral side (E), and this increase was prevented by co-injection of ECD8 (F). However, ECD8 had no effect on the endogenous ventral and dorsal β-catenin signals (compare C and D).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.