Abstract
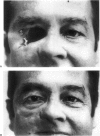
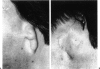
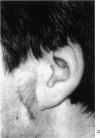
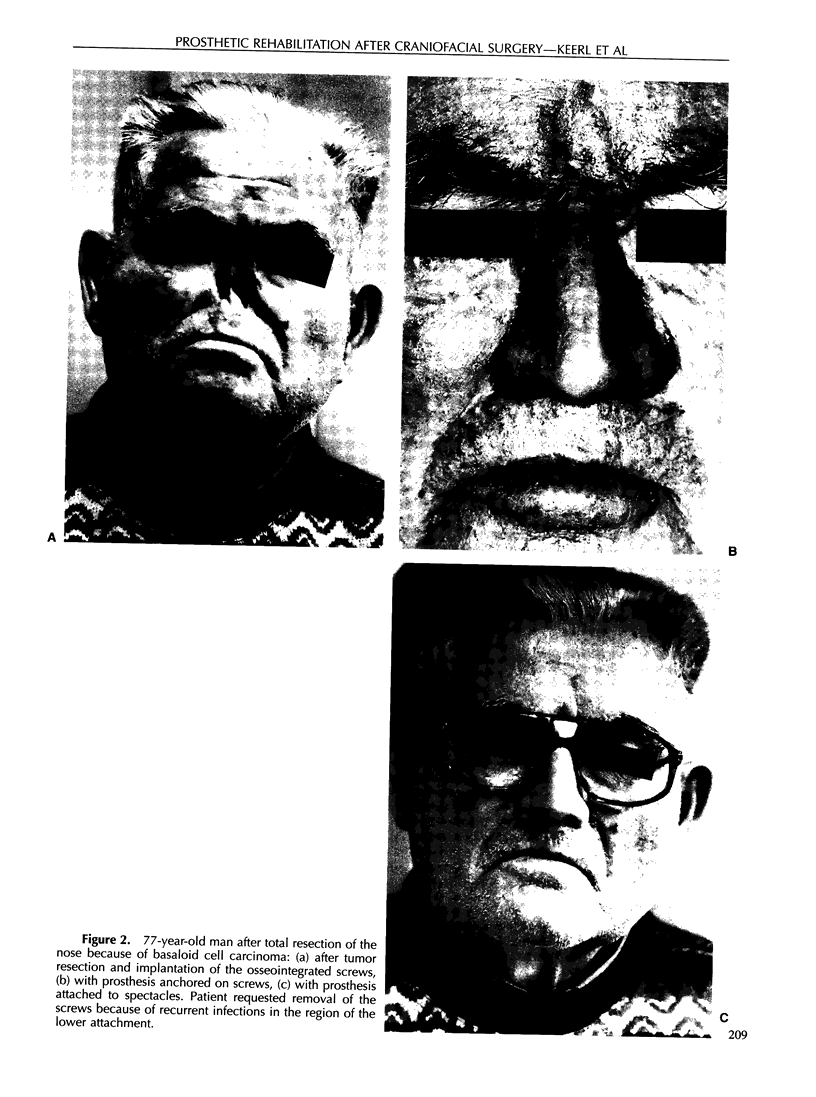
We report our experience during the last 6 years with 20 patients fitted with prosthesis (19 patients with osseointegration of screw, 1 patient with primarily gluing method) for camouflage of congenital or acquired (trauma, tumor resection) defects of the ear, nose, or eye. Out of a total of 53 extra-oral implants fitted, 3 were lost in the orbital area due to loosening 6 months after radiation treatment. Another three implants were removed at the request of an 80-year-old patient who preferred a prosthesis retained by spectacles because of recurring infection around one of the implants. On average, 43 months (range, 7 months to 8 years) after completion of the prosthesis, 85% of the patients assessed the result as excellent, 15% as good, 0% as fair, and 0% as poor. The ENT surgeon and the prosthesis designer were slightly more critical (ENT surgeon—95% good or excellent and 5% fair, prosthesis designer—90% good or excellent, 10% fair).
Full text
PDF

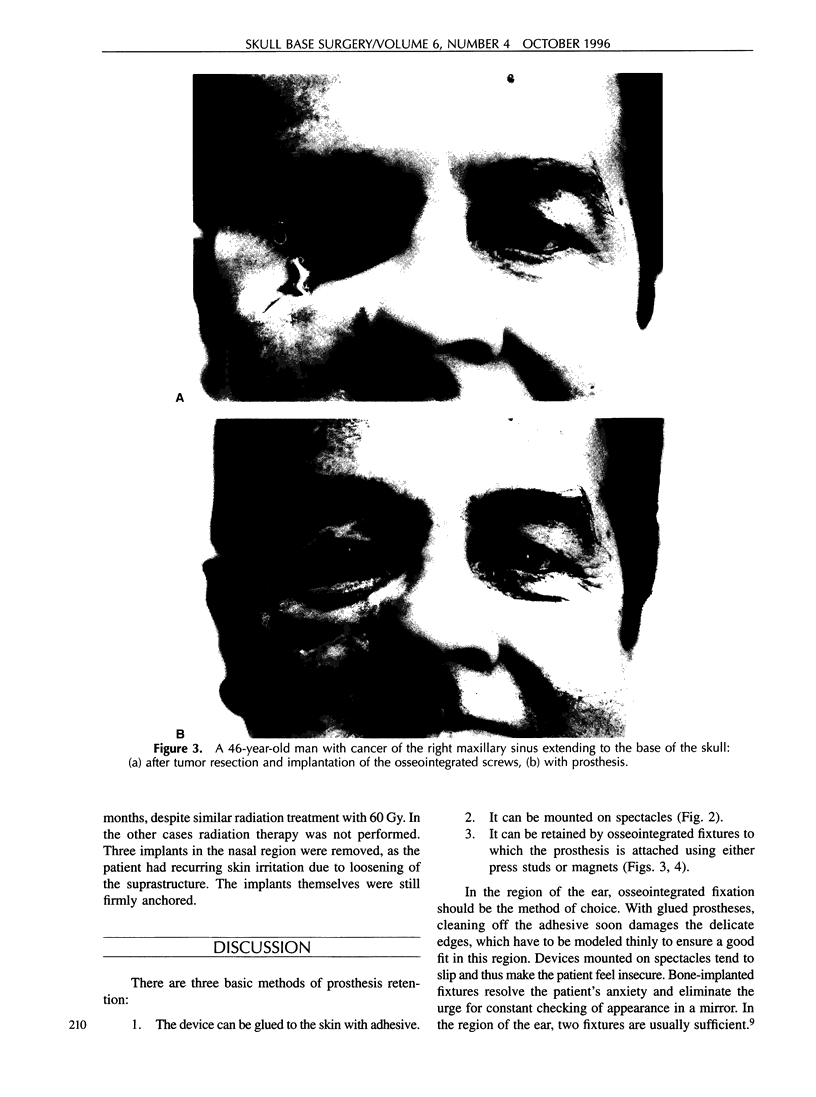
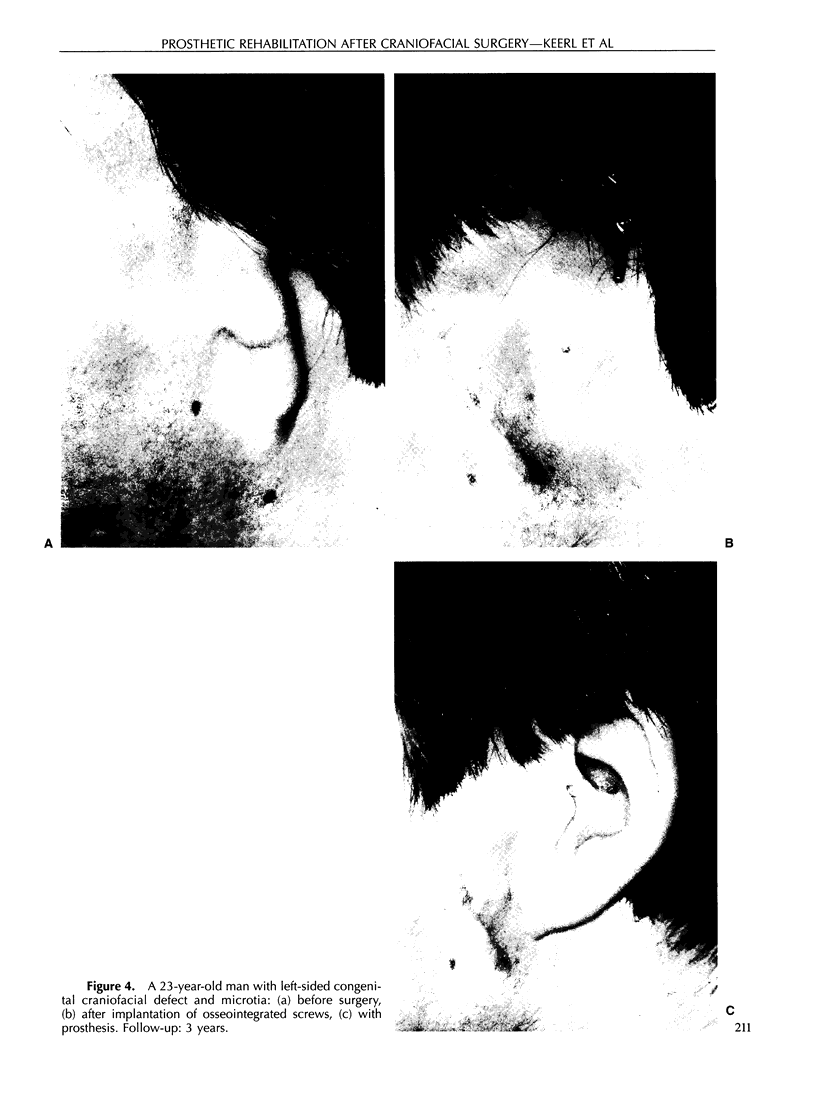


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adell R., Lekholm U., Rockler B., Brånemark P. I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981 Dec;10(6):387–416. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(81)80077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent B. The correction of microtia with autogenous cartilage grafts: II. Atypical and complex deformities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1980 Jul;66(1):13–21. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198007000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgers K. M., Bjursten L. M., Thomsen P., Ericson L. E., Tjellström A. Experience with percutaneous titanium implants in the head and neck: a clinical and histological study. J Invest Surg. 1989;2(1):7–16. doi: 10.3109/08941938909016500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtmann S., Kastenbauer E. Der Aufbau einer missgebildeten Ohrmuschel durch eine Endoprothese aus porösem Polyäthylen mit integriertem Sogsystem. Laryngorhinootologie. 1993 Jan;72(1):43–47. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-997852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson M., Albrektsson T., Tjellström A. Tissue-integrated implants in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1992 Nov;24(3):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(92)90021-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laass M., Retemeyer K., Lange K. P., Thierfelder C., Kalz W., Kirsch A., Neuendorf G., Duncan G. F. Implantologische Verankerungsmöglichkeiten bei Defektprothesen und Epithesen. Quintessenz. 1991 Nov;42(11):1725–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx R. E., Johnson R. P. Studies in the radiobiology of osteoradionecrosis and their clinical significance. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987 Oct;64(4):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(87)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parel S. M., Tjellström A. The United States and Swedish experience with osseointegration and facial prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1991 Spring;6(1):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjellström A., Lindström J., Nylén O., Albrektsson T., Brånemark P. I., Birgersson B., Nero H., Sylvén C. The bone-anchored auricular episthesis. Laryngoscope. 1981 May;91(5):811–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjellström A. Osseointegrated implants for replacement of absent or defective ears. Clin Plast Surg. 1990 Apr;17(2):355–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjellström A. Titanimplantate in der Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Heilkunde. HNO. 1989 Aug;37(8):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerda H. Reconstructive surgery of the auricle. Facial Plast Surg. 1988 Oct;5(5):399–410. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1064780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]