Figure 1.
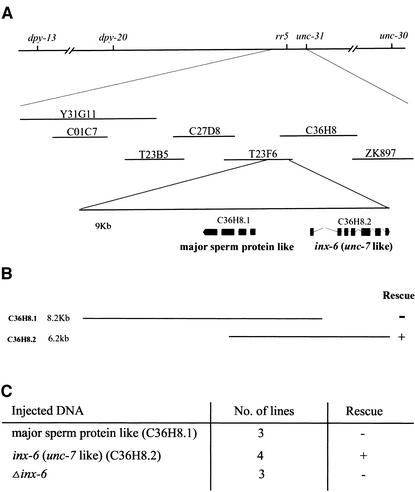
Mutation in the C. elegans inx-6 gene causes the temperature-sensitive L1 arrest phenotype of rr5. (A) Genetic and physical map of the rr5 region. rr5 maps between dpy-20 and unc-31, 0.03 map units left of unc-31. (B) Two cosmids, T23F6 and C36H8, which share 9 kb of overlapping sequence, were found to completely rescue the larval arrest phenotype at 25°C. (C) Subclones of the overlapping region were used to test for transformation rescue. The C36H8.2 subclone, which contains a predicted gene inx-6, could fully rescue the mutant phenotype, whereas a second predicted gene on this cosmid C36H8.1 had no effect. The inx-6 coding region was mutated by inserting a fragment into one of the exons, which theoretically caused a frame-shift in the predicted inx-6 coding region. The resulting Δinx-6 could no longer rescue the mutant phenotype. All constructs were injected as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS with the dominant coinjection marker pRF4 (rol-6 D).